In the last article, we introduced how to install the TouchGFX software. Here, we introduce how to use STM32CubeMX to transplant TouchGFX to the STM32 development board F429IGT6 and drive the RGB screen.
How to Transplant TouchGFX Project Using STM32CubeMX?
In this tutorial, our goal is to port the TouchGFX project to the STM32 development board.
Tools Required
- Hardware
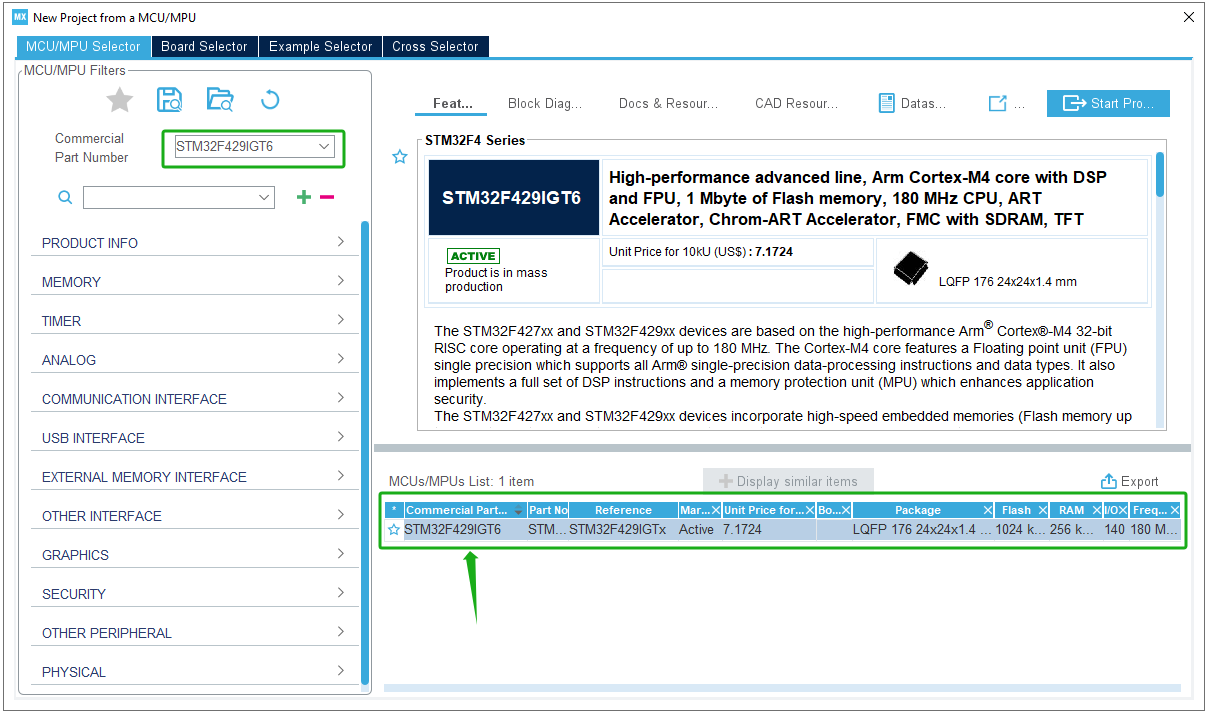
- A core board/development board based on STM32 MCU: STM32F429IGT6;
- A display with RGB interface, recommended resolution: 800*480;
- ST-Link or compatible debugger;
- Software
- ARM Keil uVision5 (version used in this article: V5.38.0.0);
- STM32 CubeMX (version used in this article: 6.9.2);
- TouchGFX Generator software package (version used in this article: V4.22.1).
STM32CubeMX Configuration
STM32CubeMX is mainly used to configure the hardware abstraction layer and middleware layer in the application framework diagram of TouchGFX.
Start a New Project:
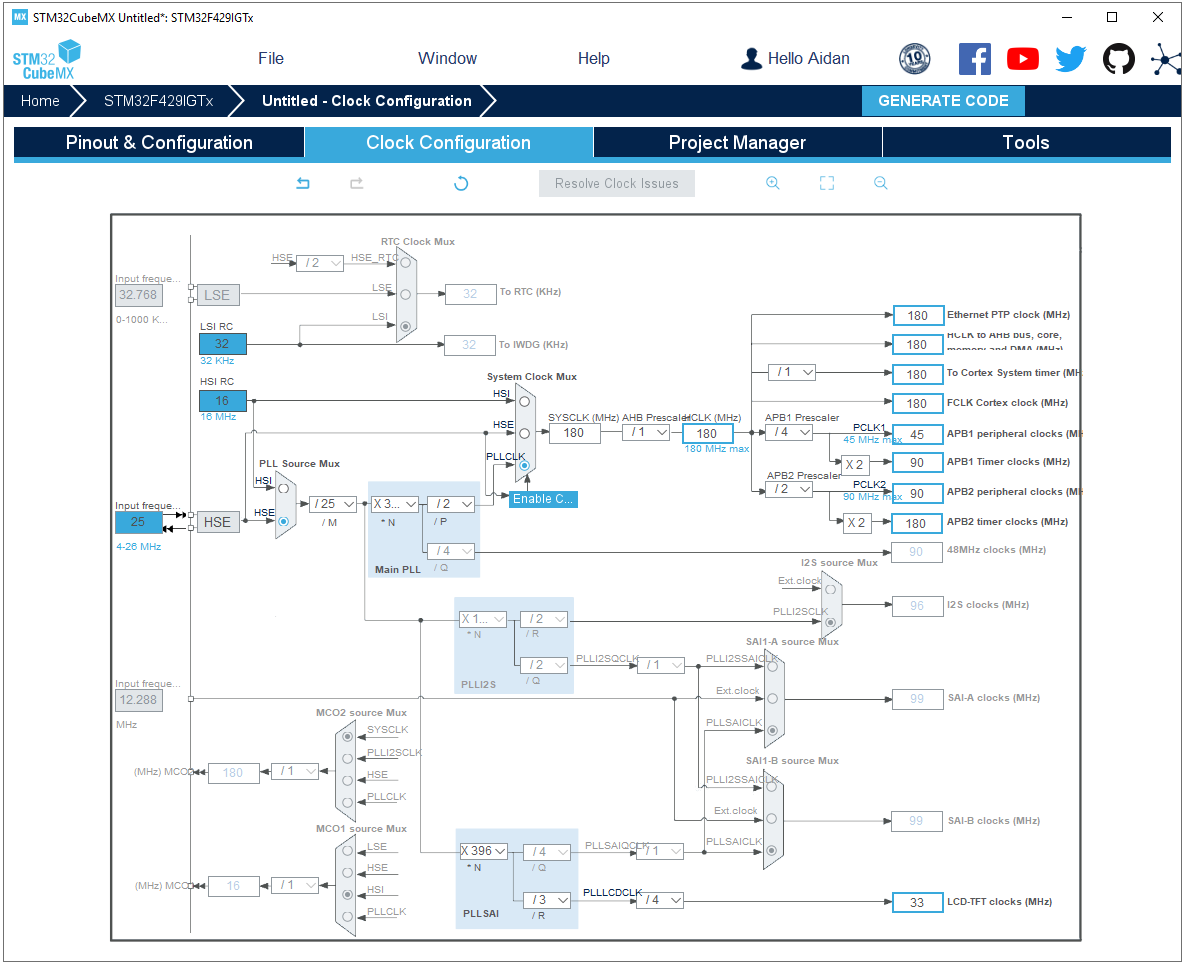
RCC system clock: High-speed external clock (HSE) configured as an external crystal oscillator.
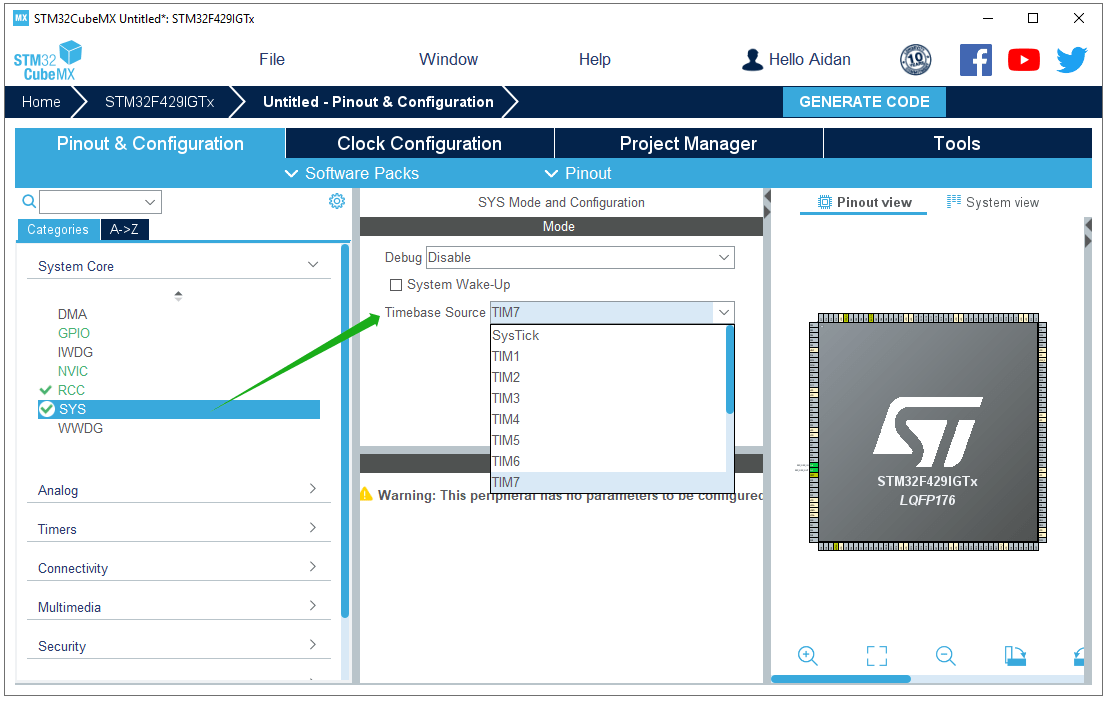
Since we need to use the FreeRTOS operating system, it is recommended to change the Timebase Source of the HAL library from SysTick to other timers. After selecting the timer, the system will automatically configure TIM, which is set to TIM7 here.
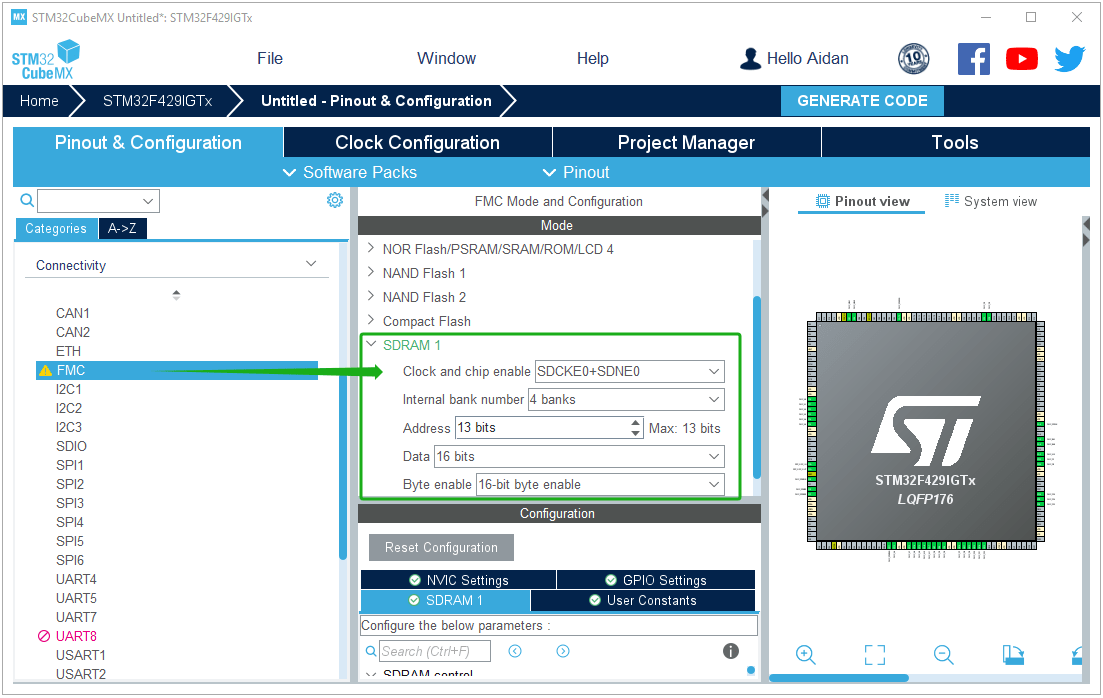
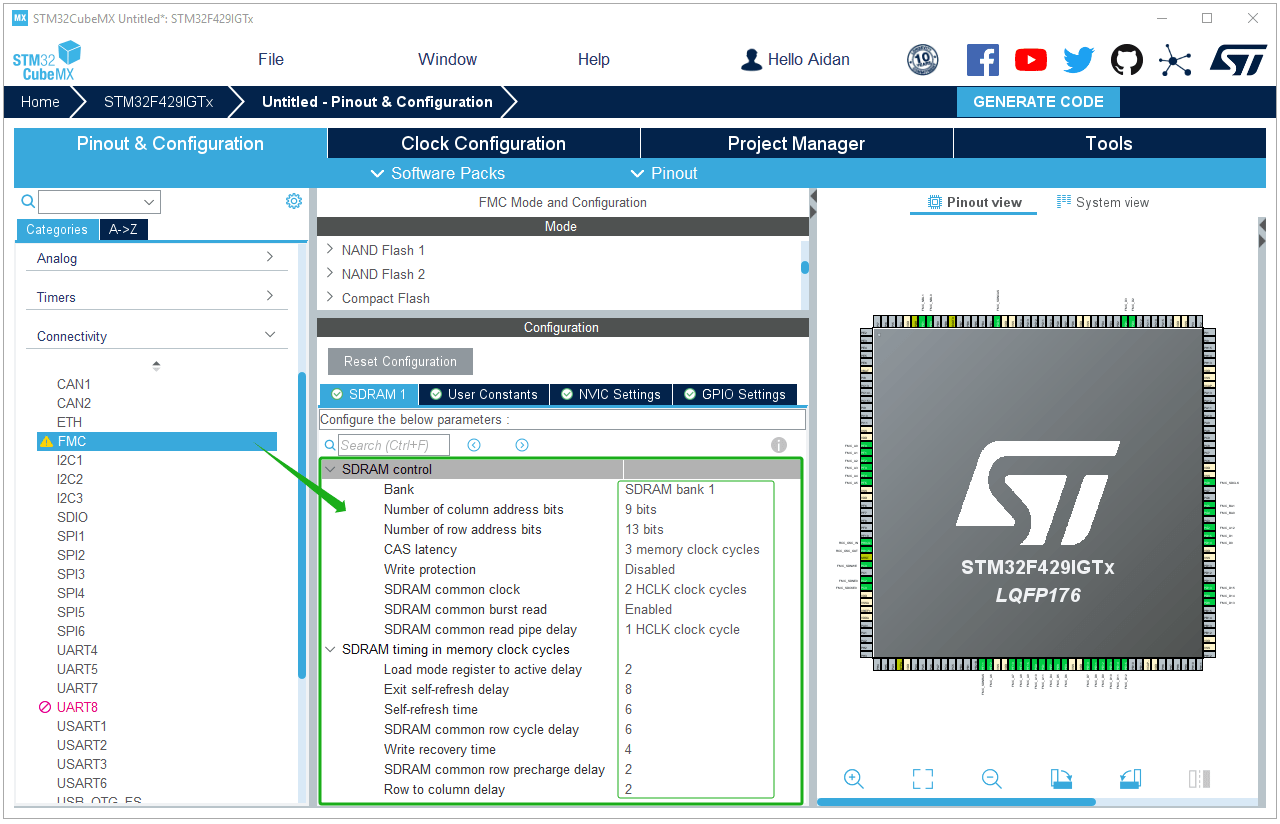
FMC settings: Configure external SDRAM as the video memory of RGBLCD, and configure parameters and pins according to your own hardware.
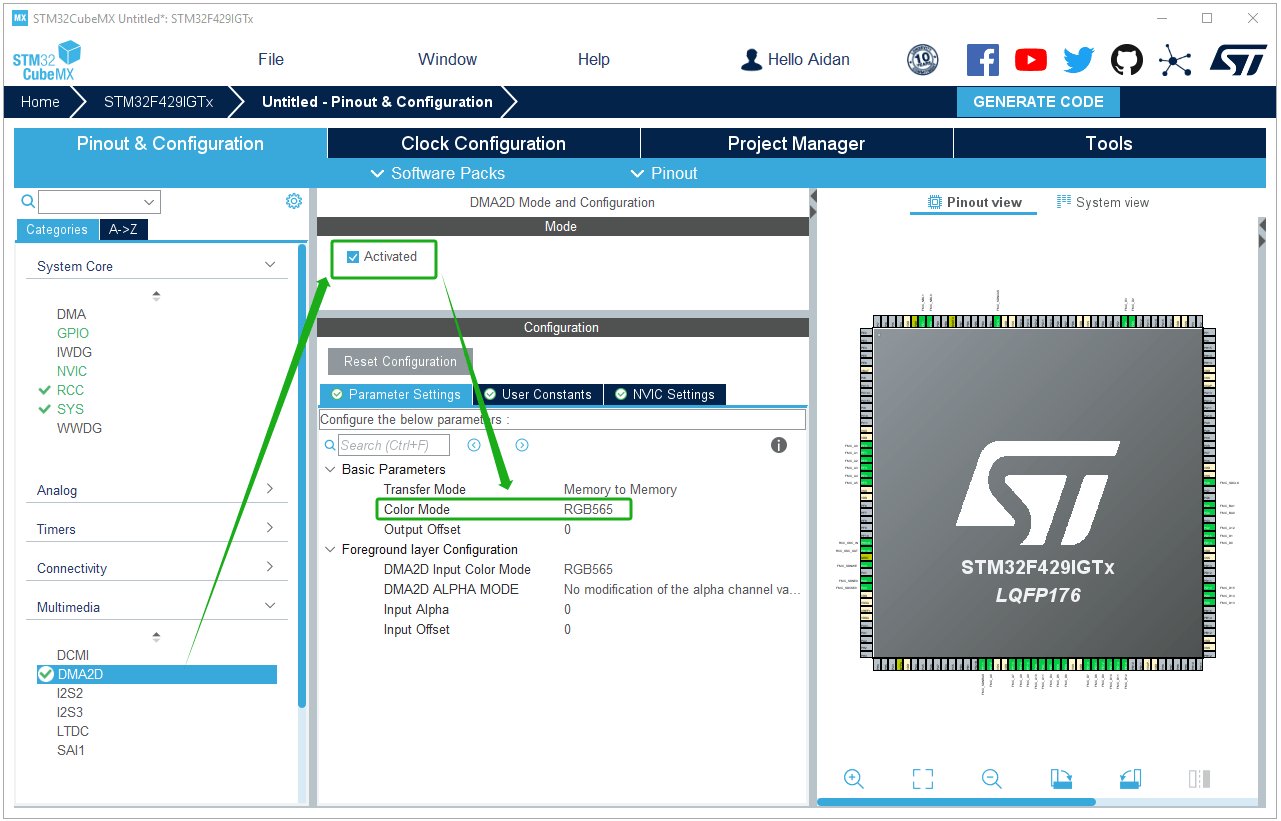
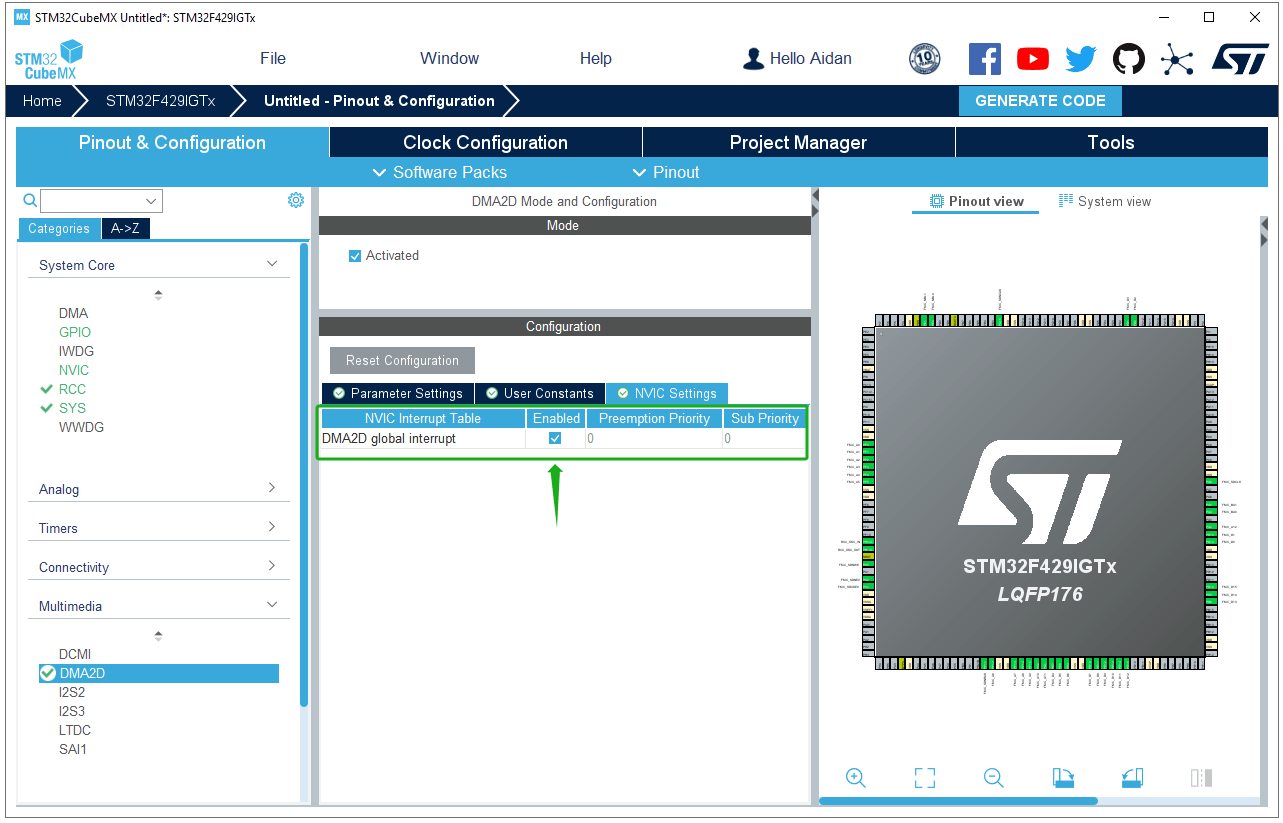
DMA2D settings: Activate DMA2D, configure the color mode to RGB565, and enable DMA2D interrupts.
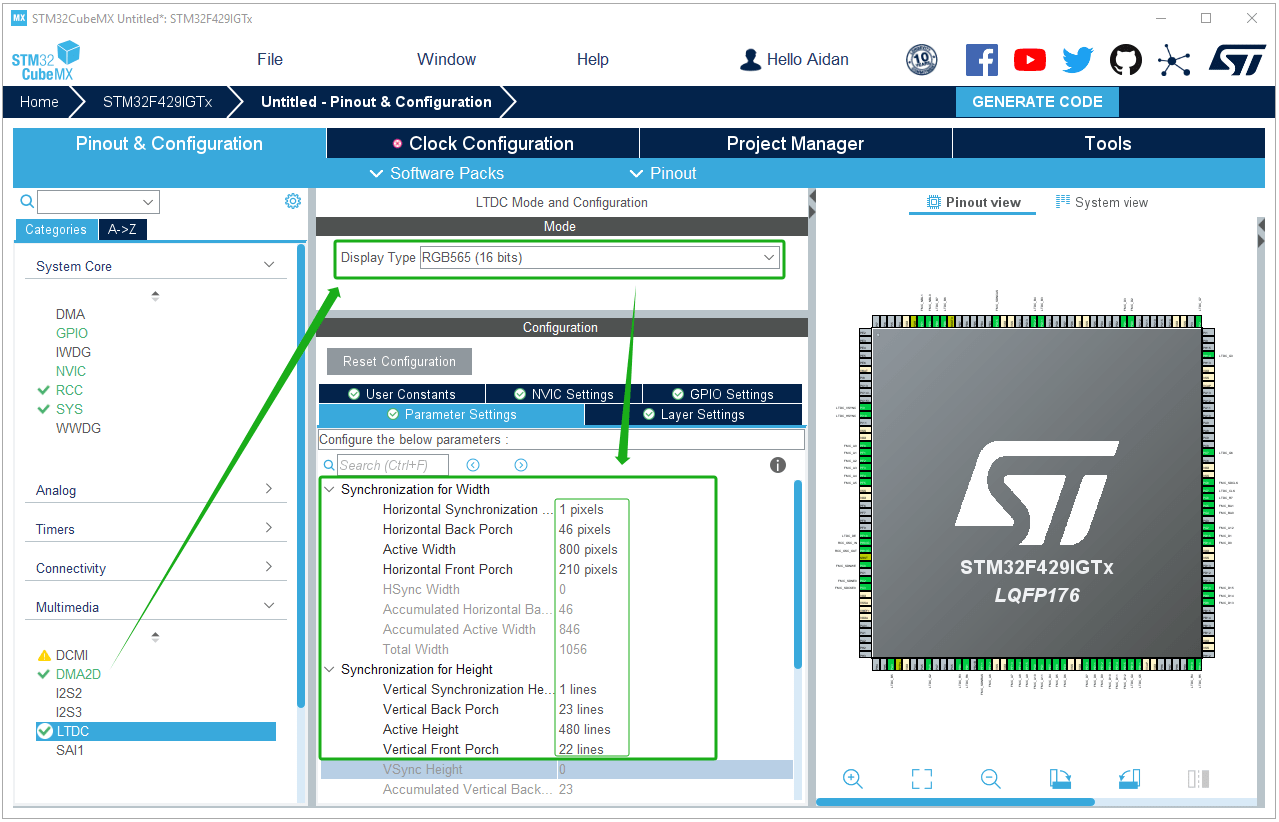
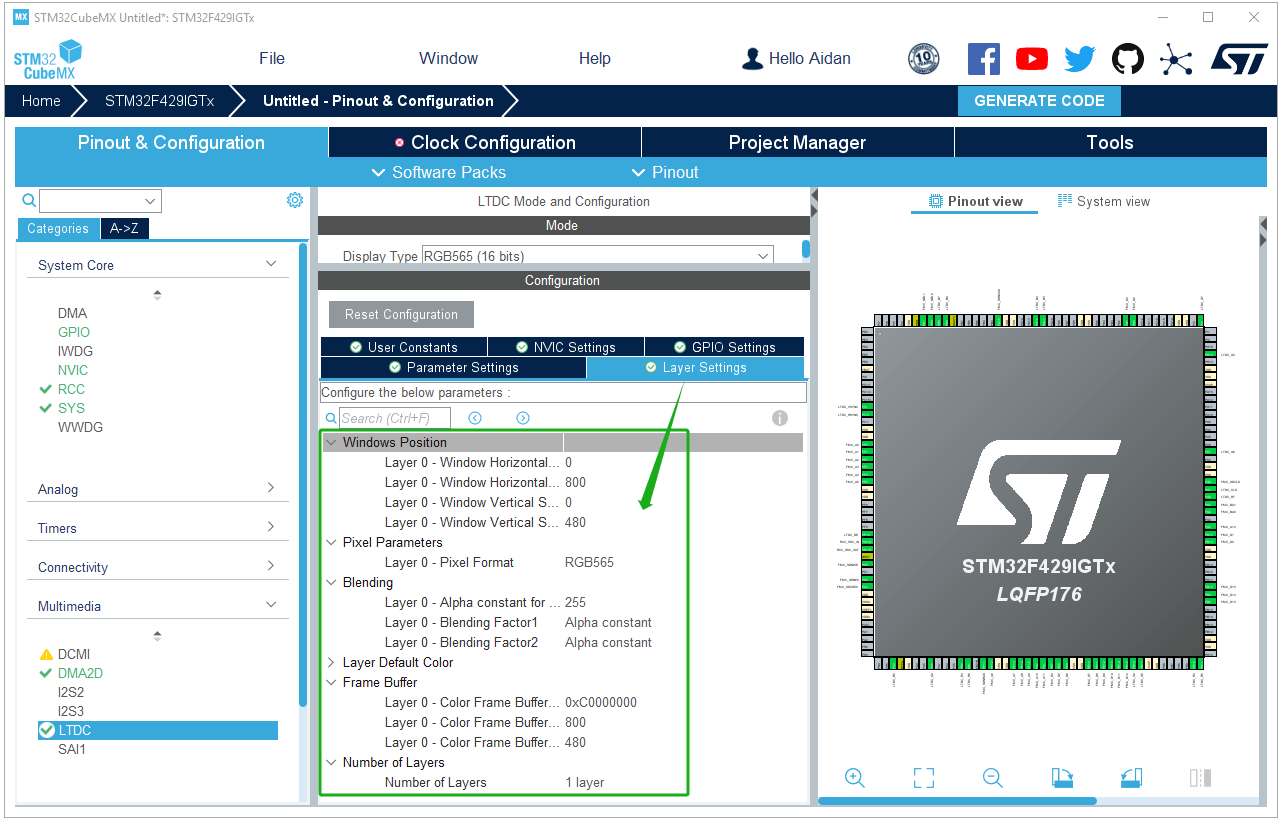
LTDC parameter settings: Configure LTDC parameters according to the screen parameters used.
LTDC layer settings: Choose to use layer 1 here, and set the frame buffer address to the first address of SDRAM 0XC0000000.
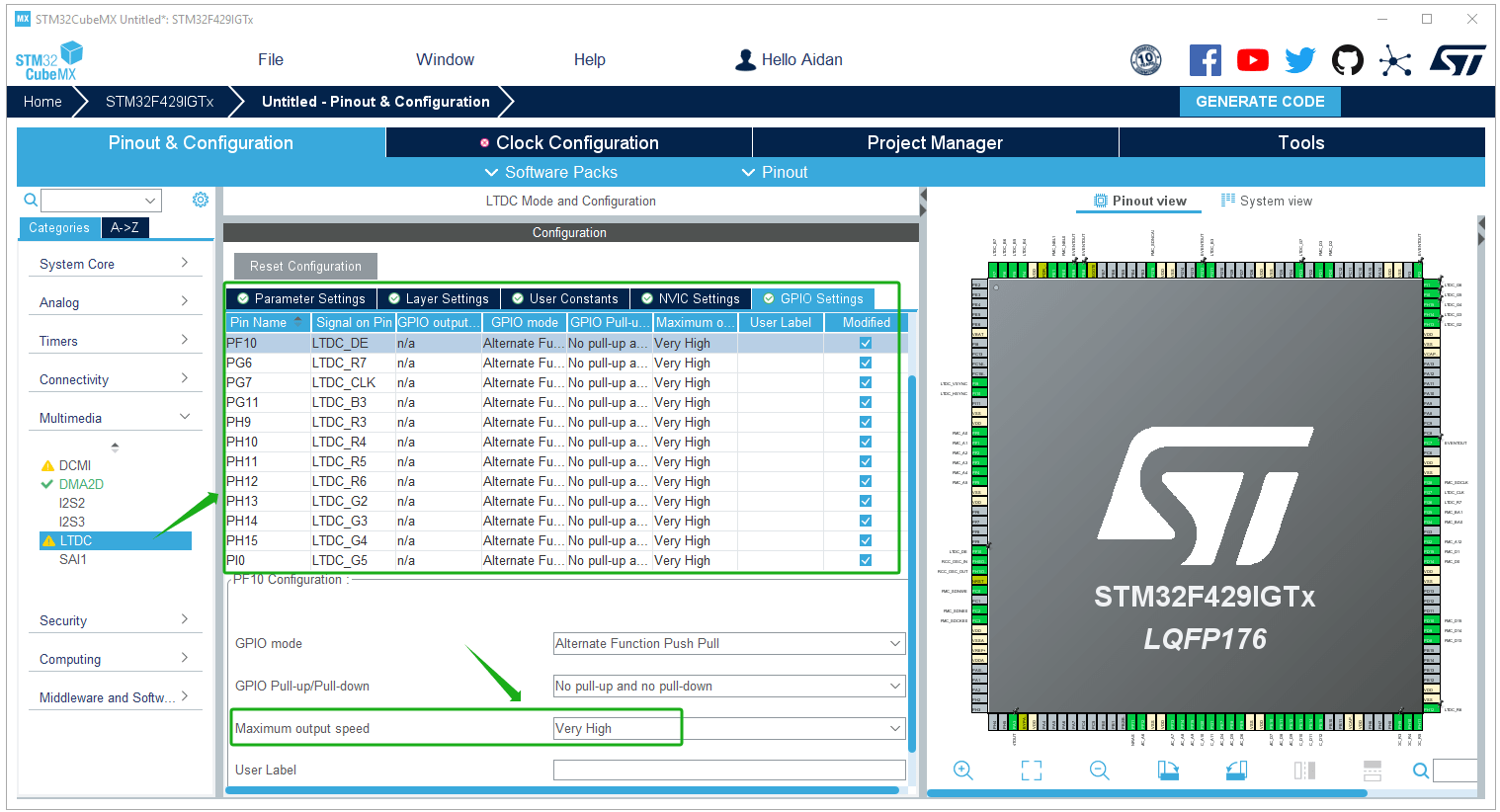
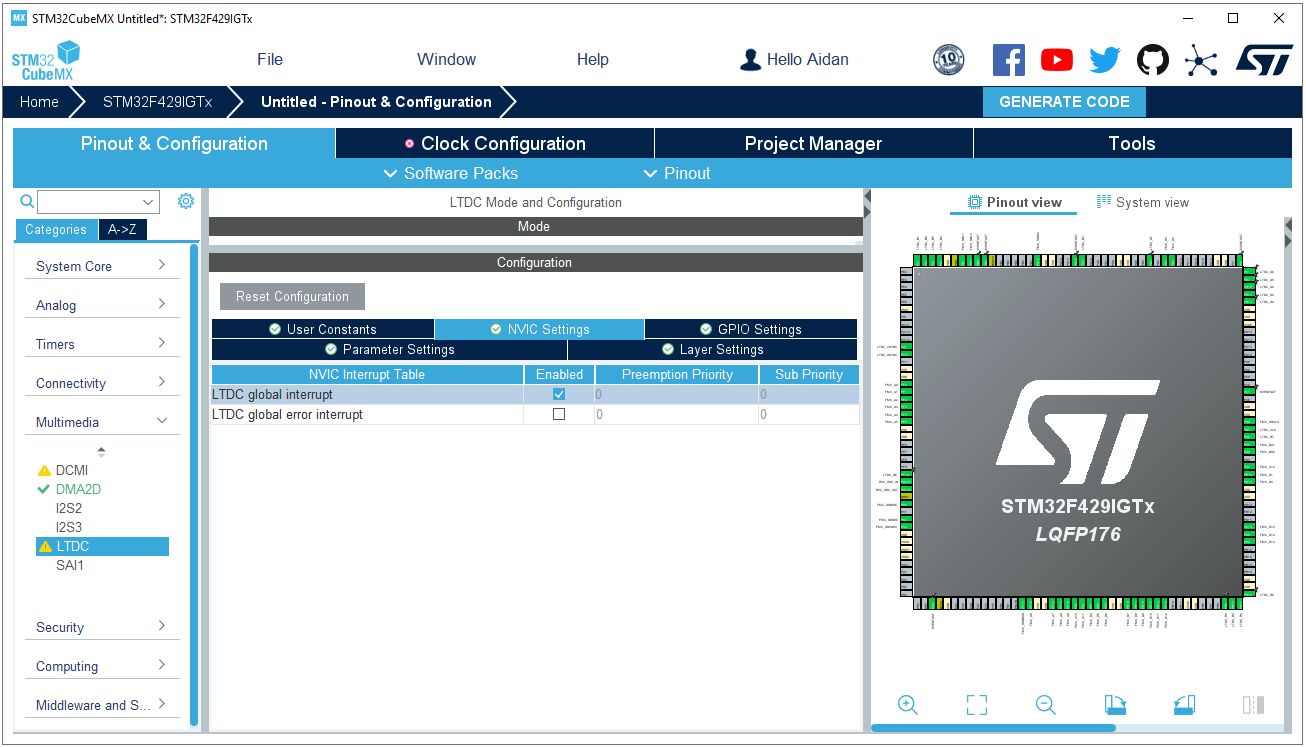
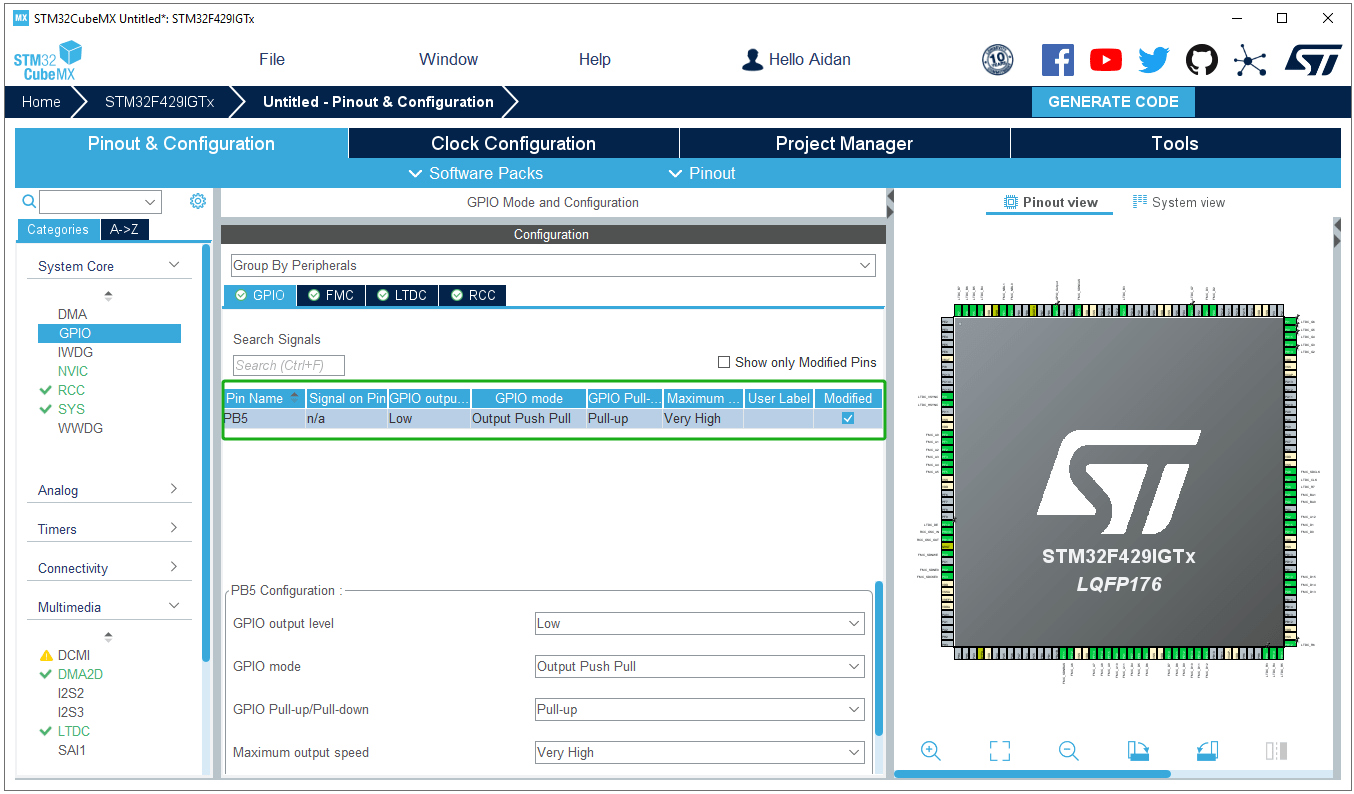
LTDC GPIO pin settings: Configure the GPIO according to the pin connections of the specific development board. Note that the output speed should be set to “Very High”; and the LTDC interrupt should be enabled.
Clock tree configuration: The pixel clock size is 1056*705*60/1024/1024=42M, the maximum pixel clock value is 42M, here it is set to 33M (1056 is the total width, 705 is the total height).
Backlight pin settings: The development board in this article uses PB5 as the backlight pin and is set to push-pull output.
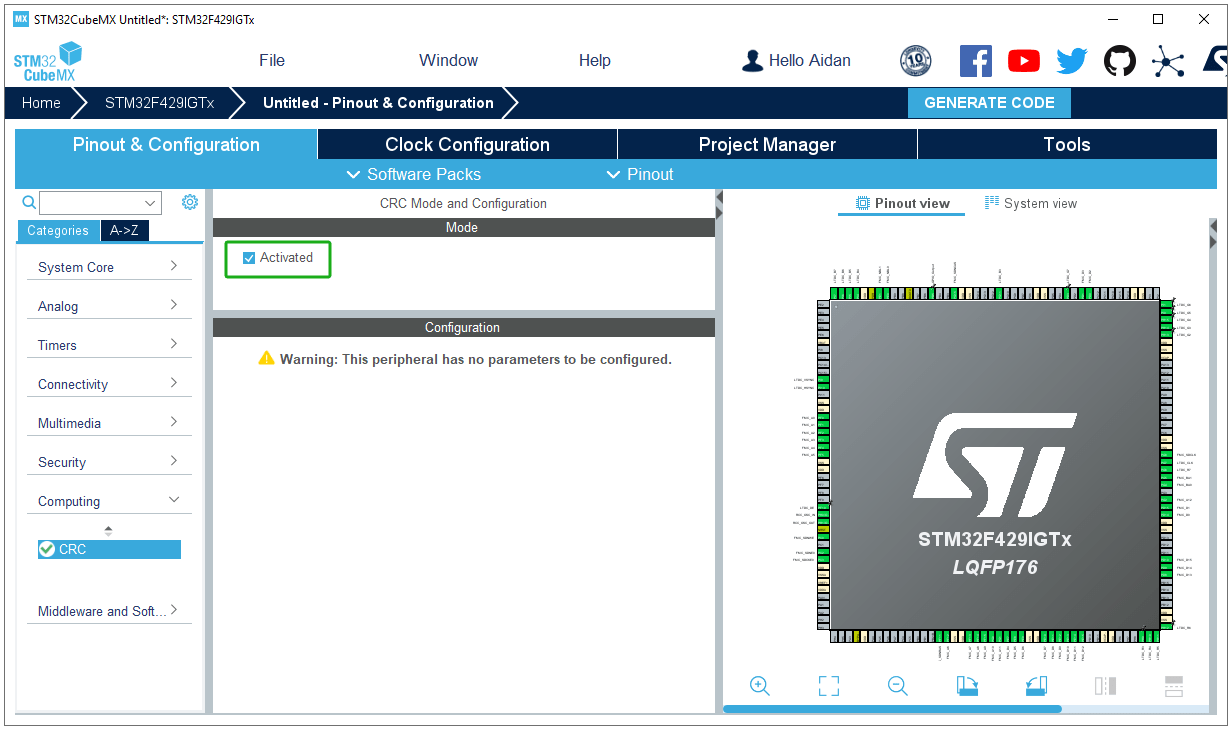
Activate CRC: TouchGFX needs to enable the CRC function.
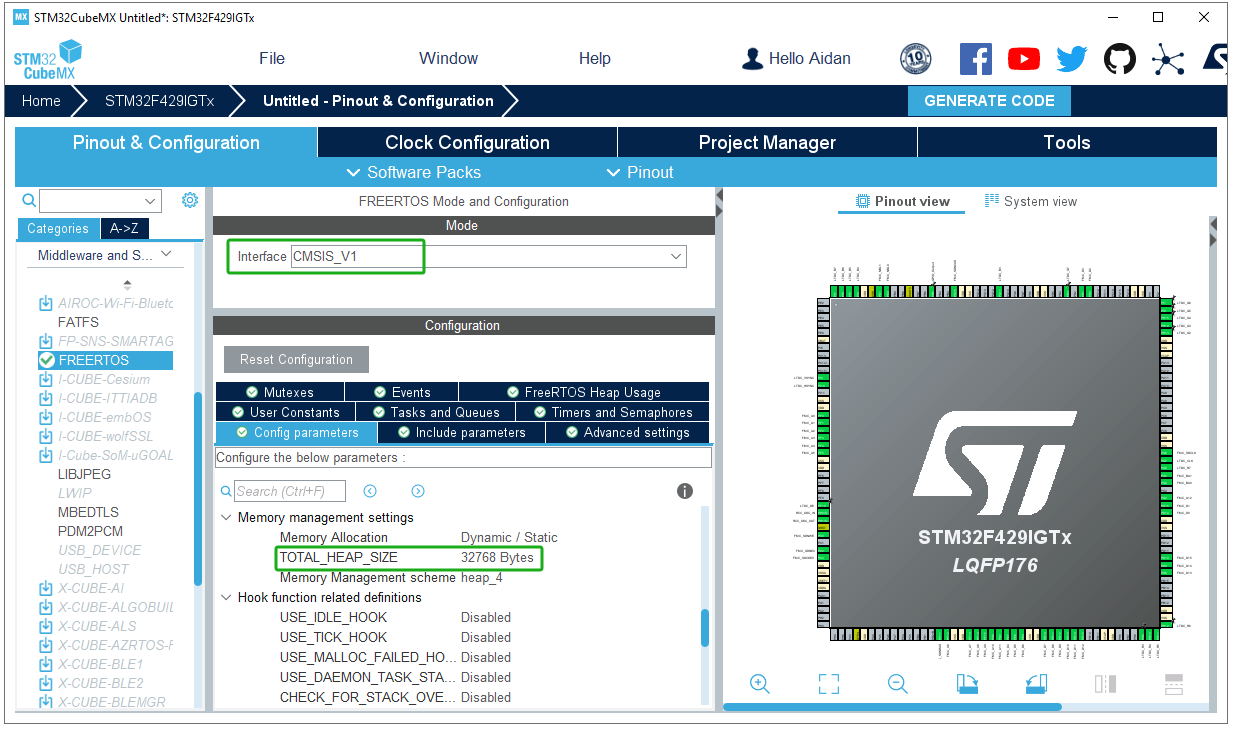
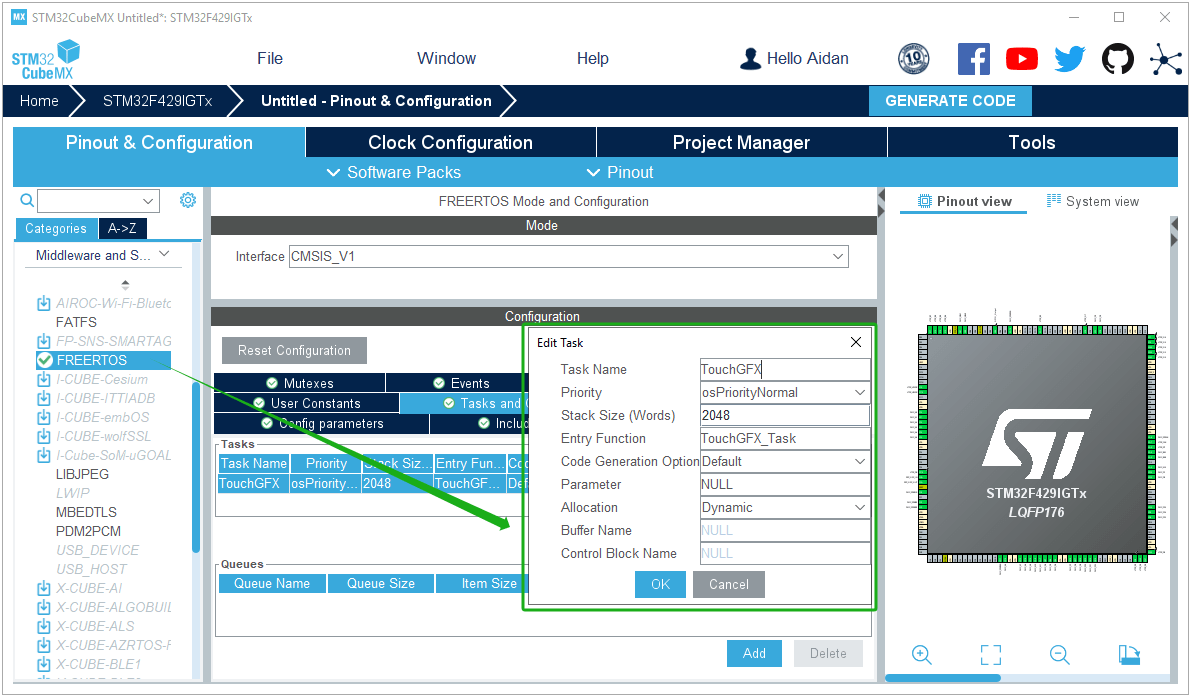
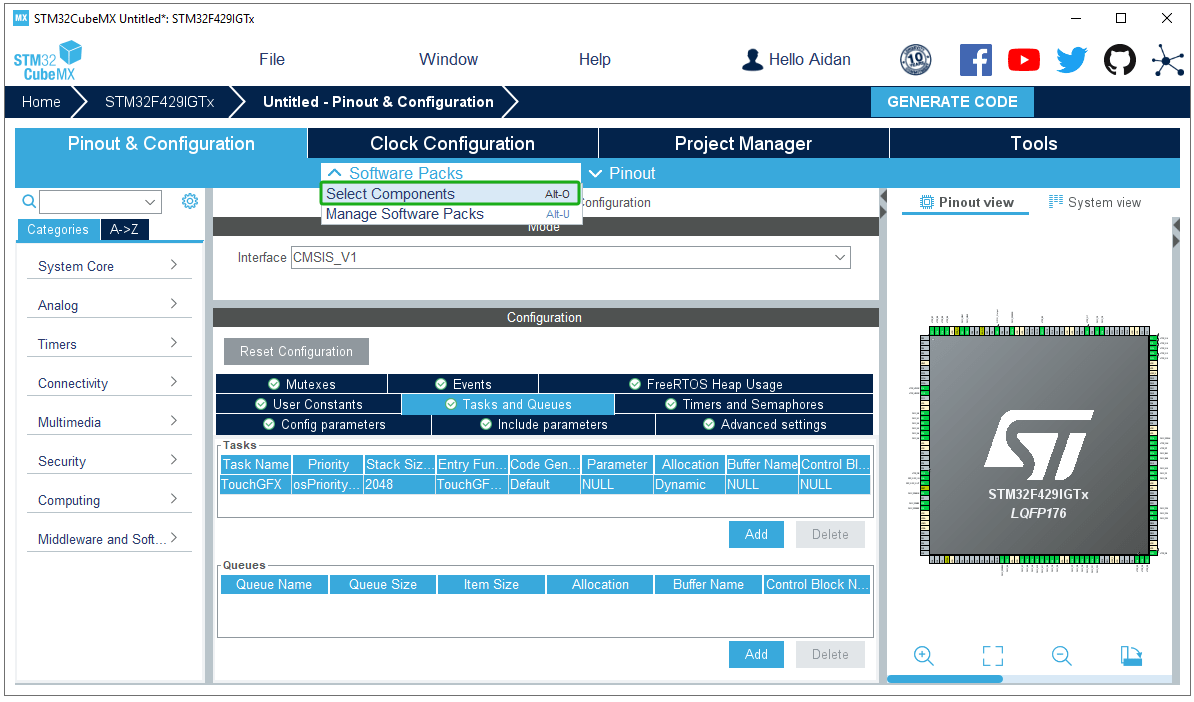
Activate the FreeRTOS system: set the heap size to 32768 bytes and the rest to default configurations; and add a TouchGFX task.
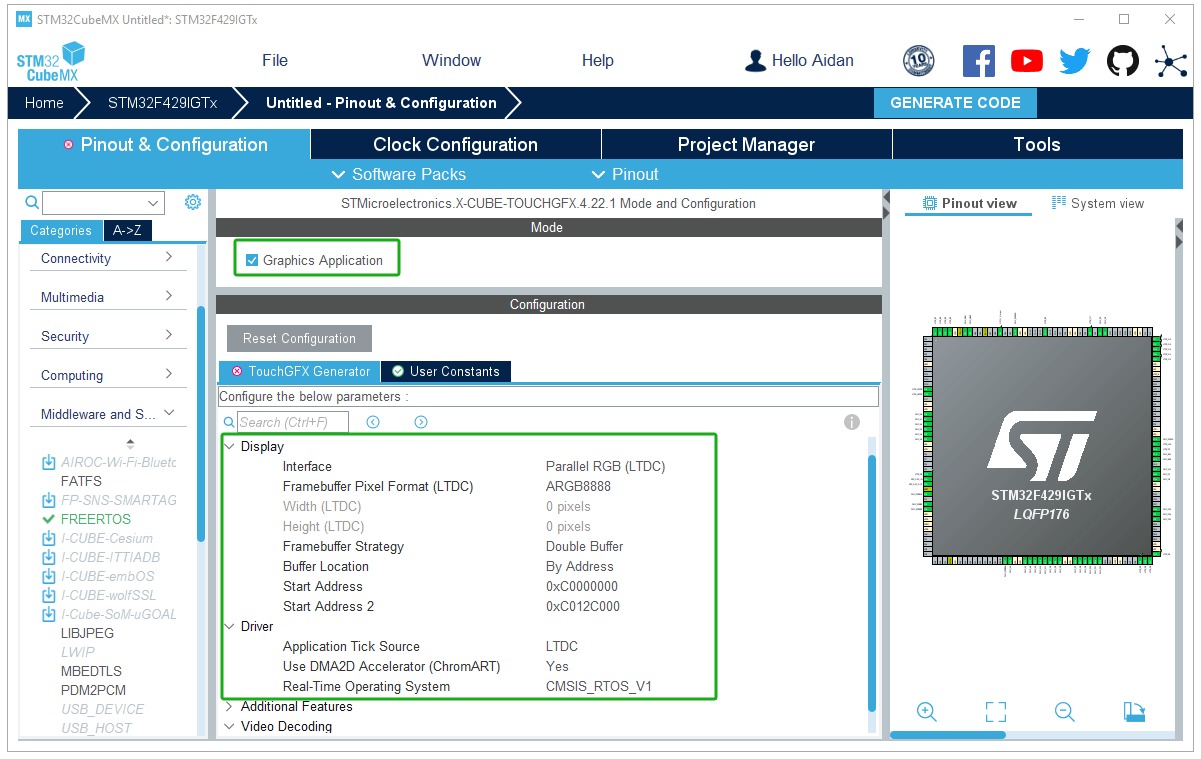
Select the Touchgfx component package.
TouchGFX parameter settings: select double buffering, RGB565, and turn on DMA2D acceleration.
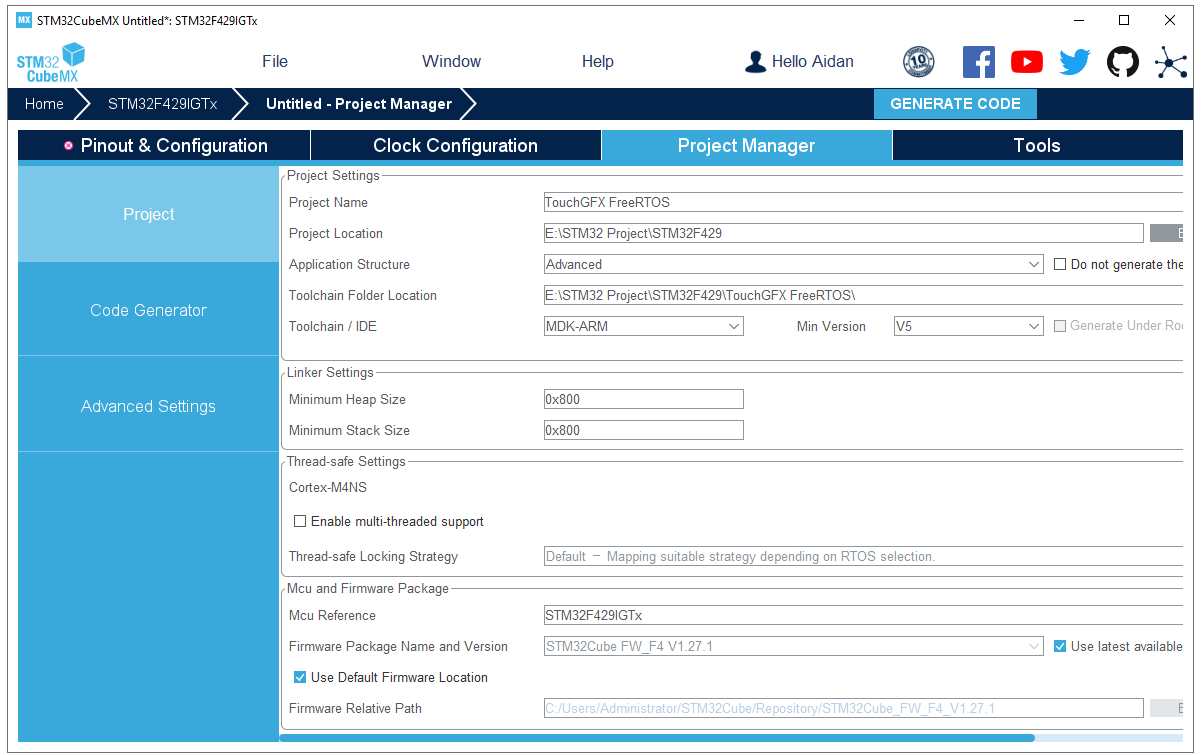
Project Manager: setting the project name, project location and linker. (The minimum stack size is set to 0X800.)
Generate project code: After STM32CubeMX generates the project, don’t open the Keil project. (If you compile the Keil project at this time, a large number of errors will appear.)
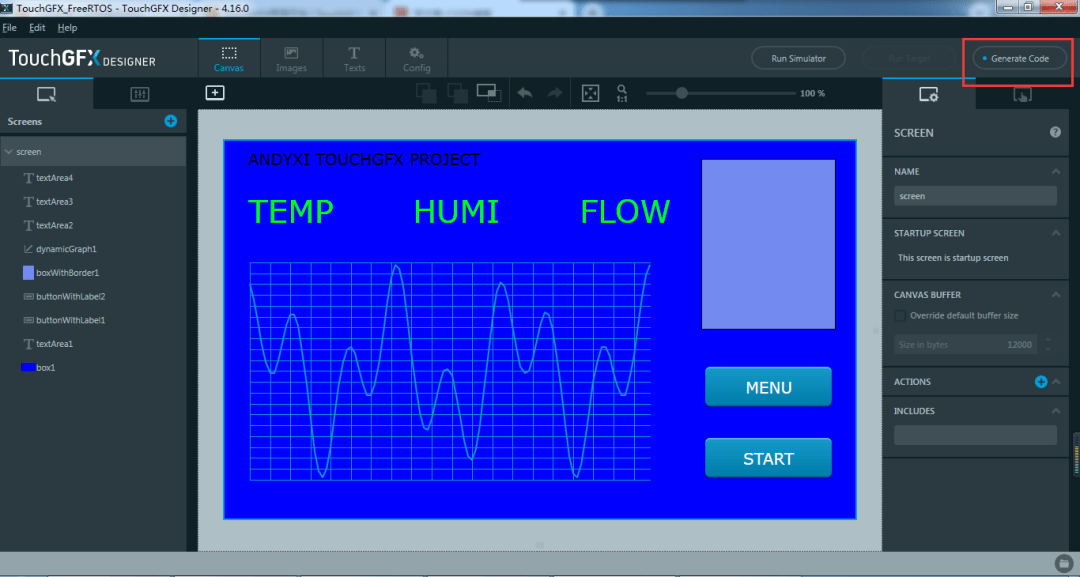
TouchGFX Designer
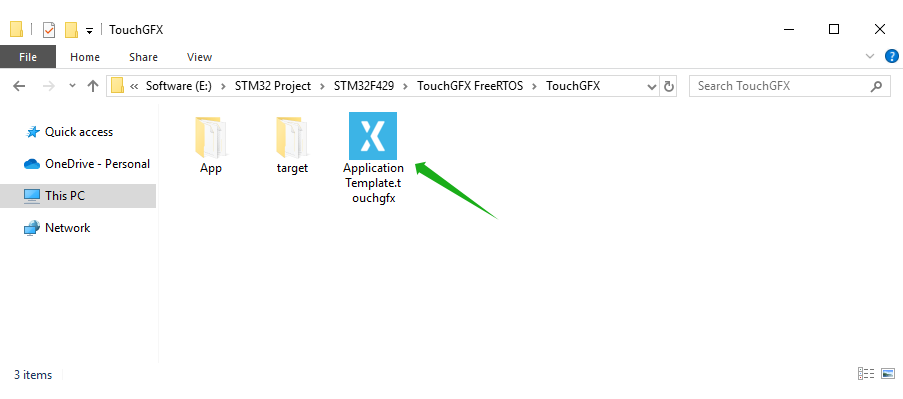
After the Keil project is generated, The Code is successfully generated under:
E:/STM32 Project/STM32F429/TouchGFX FreeRTOS
We find this path. There is ApplicationTemplate.touchgfx.part in the TouchGFX directory. Click to open TouchGFX Designer to design the UI.
After dragging and dropping some controls and clicking Generate Code to generate the code, the TouchGFX related code will be automatically added to the project.
MKD-ARM Keil Compile
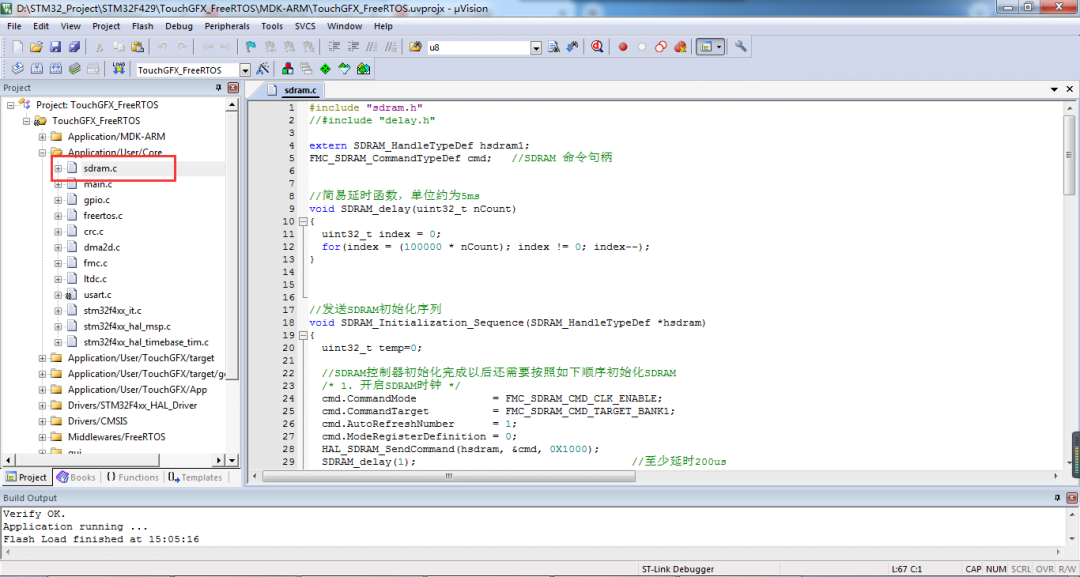
Add SDRAM driver source files and header files.
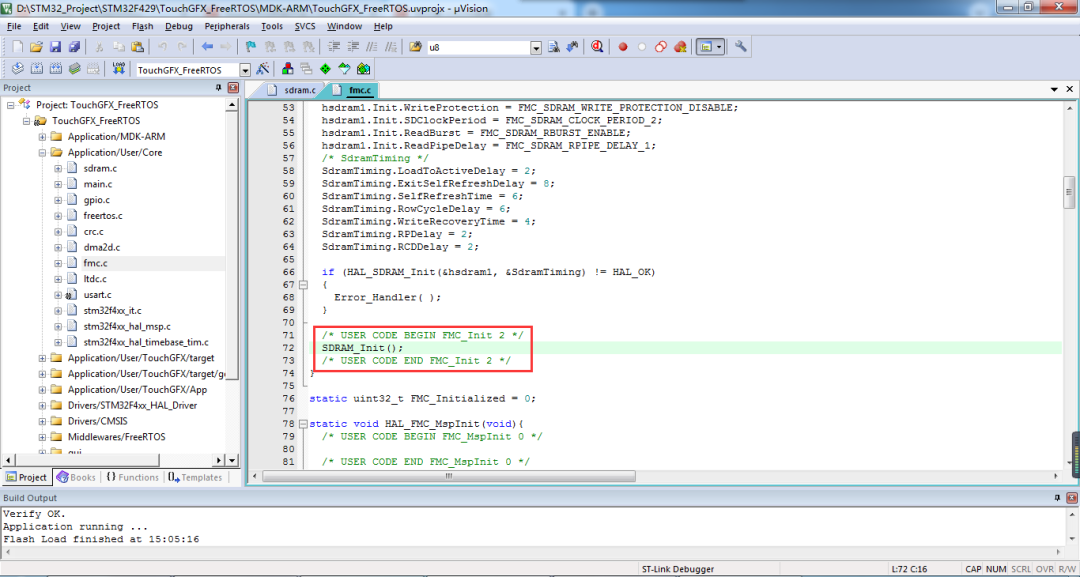
Add the SDRAM initialization function in the MX_FMC_Init() function of the fmc.c file to drive the external memory chip.
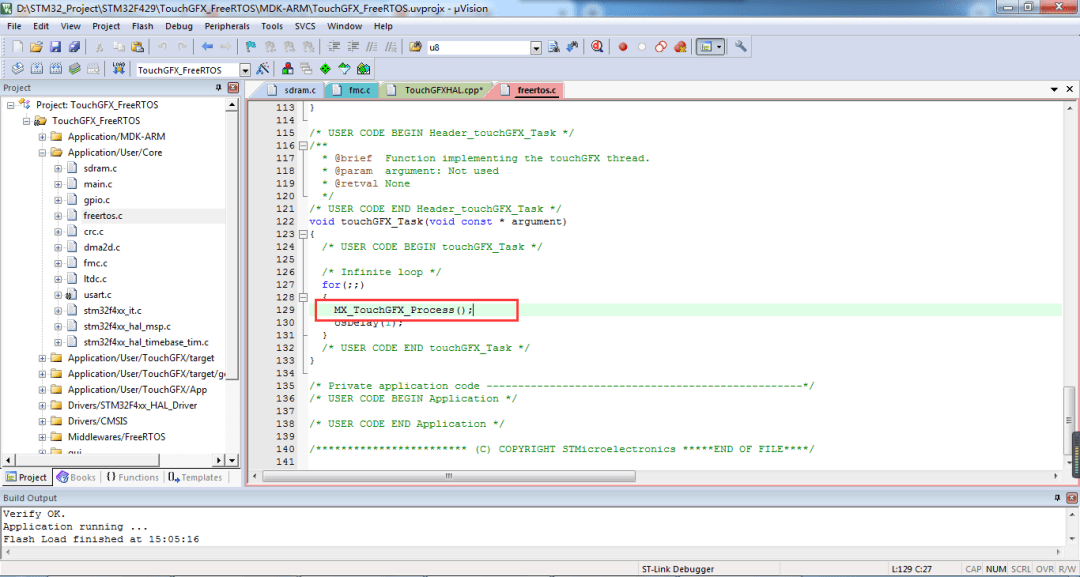
Turn on the screen backlight in the touchgfxhal.cpp file.
Add the corresponding task and add the TouchGFX processing function.
Download and Test
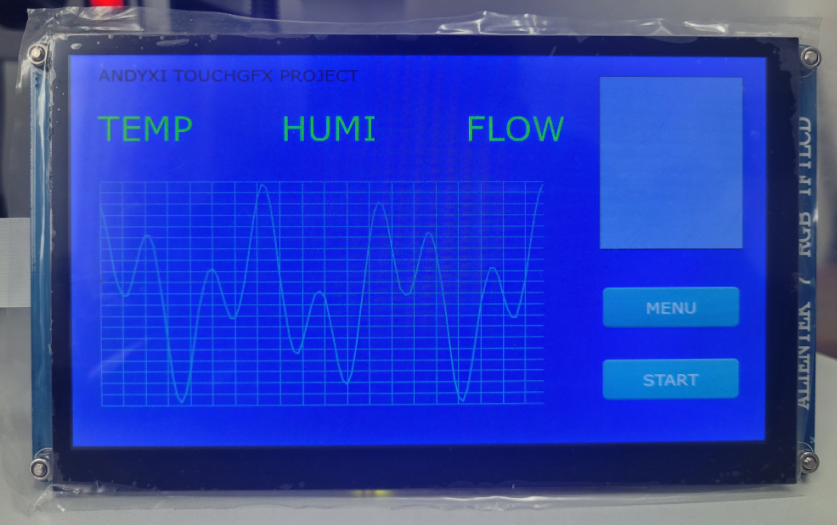
After compilation is correct, download it to the development board.
If TouchGFX is transplanted successfully, the development board screen will display the interface designed in TouchGFX Designer.