According to the UN’s “Global E-waste Monitor 2020” report, the total amount of e-waste generated globally reached a record 53.6 million metric tons in 2019. It is forecast to reach 74 million tons in 2030. And more and more new circuit boards are produced and used, which means that a large number of old circuit boards are scrapped and eliminated.
Generally speaking, the common metals (aluminum, copper, Iron, nickel, lead, tin and zinc, etc.), precious metals (gold, palladium, platinum, silver, etc.) and rare metals (rhodium, selenium, etc.), but because the circuit board substrate itself is made of glass fiber and epoxy resin Yes, these materials have little recycling value and are difficult to recycle. They are often simply landfilled, incinerated or piled up, which will cause a great waste of resources and environmental pollution.
The PCB substrate-Soluboard developed by Jiva Materials is expected to solve this problem. In this post, let’s introduce what’s the soluboard, how does it work and it’s disadvantages.
What is Soluboard?
According to reports, Soluboard is a recyclable, biodegradable printed circuit board (PCB) substrate based on natural fibers and halogens, developed by British startup Jiva Materials. It is a new type of PCB substrate, made of natural fibers wrapped in a halogen-free polymer, which is different from the FR-4 substrate often used in the industry. This material can be dissolved in layers as long as it is soaked in hot water at about 90 degrees Celsius for 30 minutes, so that the components that were originally soldered on the circuit board can be completely separated for recycling. The remaining fibers and polymers are non-toxic and can be composted, and the remaining solution can also be disposed of using standard domestic wastewater systems.
“Using a water-based recycling process can improve recovery of precious metals,” said Jonathan Swanston, CEO and co-founder of Jiva Materials. “Furthermore, replacing FR-4 PCB material with Soluboard will result in a 60% reduction in carbon emissions, more specifically In other words, 10.5 kilograms of carbon and 620 grams of plastic can be saved per square meter of PCB.”
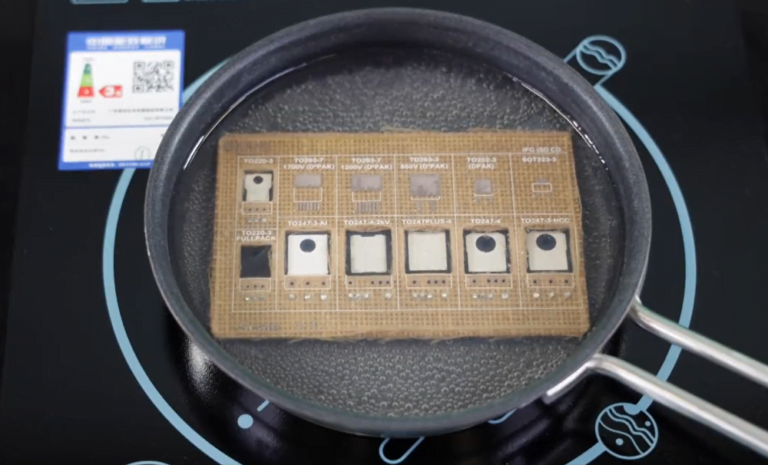
At present, Infineon has reached a cooperation with Jiva Materials, using Soluboard to produce three different demonstration boards, and plans to expand its product range in the next few years. It has already been used in more than 500 devices, showcasing the company’s portfolio of power discretes, including a circuit board with components designed for refrigerator applications. Based on the results of ongoing stress tests, Infineon plans to provide guidance for the reuse and recycling of power semiconductors removed from Soluboard, which can extend the service life of electronic components.
How does Soluboard Work?
How is Soluboard biodegradable and recyclable? The halogen-free flame retardant impregnated natural fibers in Soluboard are encapsulated in a non-toxic polymer, which will dissolve when immersed in hot water at 90°C for 30 minutes. The dissolved polymer solution can be used for normal wastewater treatment, the electronic components on the PCB board will be separated, and the remaining natural fibers can be reused as fertilizer.
In the video explanation of the biodegradable and recyclable Soluboard PCB board launched on Jiva’s official website, the organic material of the Soluboard PCB substrate is immersed in 90 ° C for 30 minutes, and the electronic components are easily separated. With the dissolution of the polymer, the The fibrous material begins to delaminate and can be easily torn apart like paper.
However, although the glass fiber and epoxy resin used in the traditional PCB in Soluboard have been replaced by natural fibers and polymers soluble in hot water, this does not mean that Soluboard will “dissolve” when it is splashed with any liquid , but need a lot of hot water and a long time to degrade.
There are also many restrictions on the conditions for its degradation. For example, the Soluboard printed circuit board needs to be immersed in 90°C water (close to the boiling point) for 30 minutes to decompose the product. After Soluboard decomposes in hot water, it can be recycled very easily – metals, components, natural fibers and polymer solutions. Polymer solutions can be processed through domestic wastewater treatment, fibers can be composted or reused, and metals and components can be recycled or reused.
In this regard, Andreas Kopp, Head of Discrete Product Management, Green Industrial Power Division, Infineon, said: “For the first time, recyclable and biodegradable PCB materials are used in the design of electronic products for consumer and industrial applications, which is a milestone towards a green future. “We are also actively researching the end-of-life reusability of discrete power devices, which will be another important step in driving a circular economy in the electronics industry.”
Disadvantages of Soluboard
Soluboard costs 50%-75% more than current PCB substrate materials. However, if the Soluboard material can be produced in volume, its price will be similar to that of traditional PCB materials. Dr. Swanston said that the annual production scale of traditional PCB materials exceeds 250 million square meters. If Soluboard can be produced on this scale, its price will be the same.
Soluboard can currently only be used to manufacture printed circuit boards with a single layer of traces on one or both sides, while complex products may have multiple layers of traces with insulation between them. Jiva has a technology roadmap for making laminates suitable for multilayer boards, although it is not expected to supply this market for the next few years.
Work hard on PCB board materials, and the development of biodegradable technology has indeed attracted the attention of the market, but the current Soluboard PCB is only suitable for low-reliability consumer electronics products. For PC or server systems with multi-layer motherboards, does not apply.
PCB characteristics include heat dissipation, fire resistance, and mechanical stability (should not be easily cracked), etc. Whether Soluboard, a water-soluble material, is competent is questionable.
But Swanston said he believes Soluboard will likely be used in most board designs in the future. “It can be used in most rigid PCBs in single-sided and double-sided commodity boards today and in multi-layer PCBs in the future. It is not suitable for flexible circuit boards.”
FAQ
Is Soluboard susceptible to moisture?
Jiva said that Jiva is ensuring that Soluboard is compatible with water-based PCB manufacturing processes. Jiva also designed the Soluboard to withstand high humidity environments.
Is there technical data available for Soluboard?
Jiva said it is thoroughly testing Soluboard to ensure it meets the technical requirements expected by the PCB industry.
How is the circuit applied to Soluboard?
Jiva says it is optimizing Soluboard to work with both additive (conductive silver ink and copper sintering) and subtractive (traditional copper foil etching) methods.