Single-sided PCB, also known as “single-layer PCB”, was first used in industrial applications in the early 1950s. Due to its simple design principles and manufacturing processes, it still occupies an important position in the history of PCB production and manufacturing. Single-sided PCB has only one side covered with copper, with components on one side and circuitry on the other. From top to bottom, single-sided PCBs usually consist of solder mask layer, copper layer, and insulating material.
Features of Single-sided PCB
Since single-sided PCBs only have one side for circuitry and cannot be connected between the two sides, they require a larger area to accommodate the same number of components compared to other PCBs. Therefore, they are more suitable for designs with lower requirements for component distribution density.
Although the design of single-sided PCBs is simpler than other types of PCBs, their characteristics of only distributing components on one side make them more stringent in terms of wiring and component placement design. For example, the solder pads of single-sided PCBs must be large, otherwise problems may occur during soldering and repair processes. The routing of the circuit board cannot cross and can only be designed along their respective paths.
Manufacturing Process of Single-sided PCB
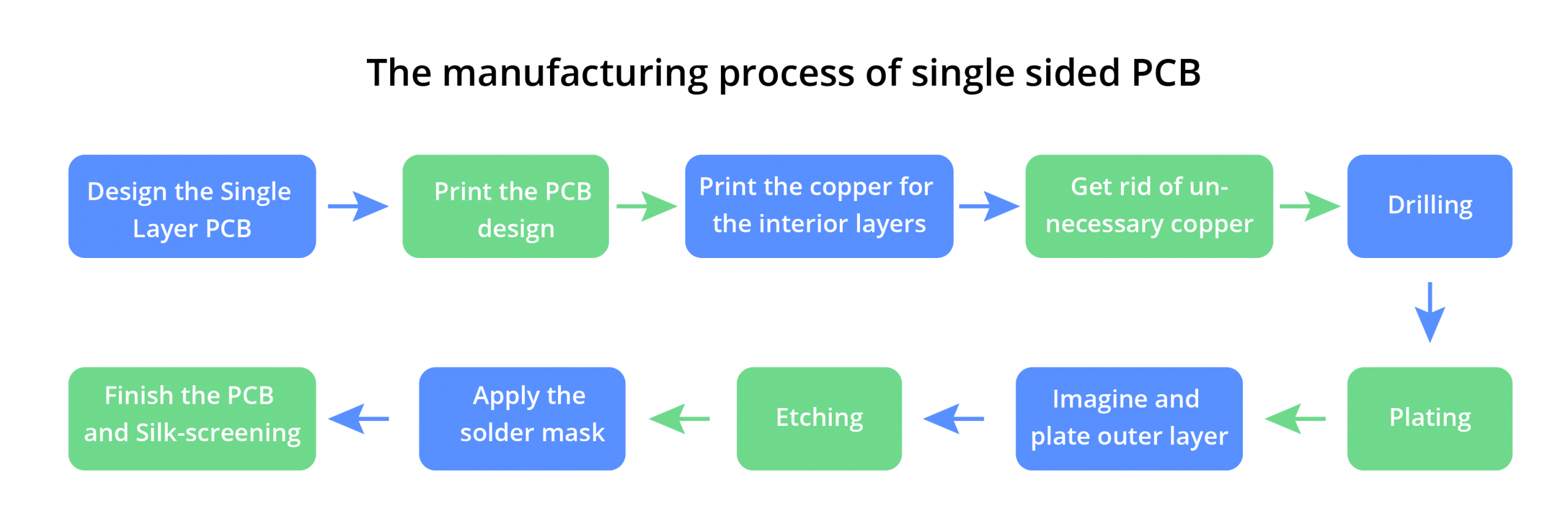
Compared with other types of PCBs, the production process of single-sided PCBs is simpler and in most cases, the cost is lower. The general main processes are:
- material cutting
- drilling
- circuit processing
- etching
- AOI
- solder mask
- printing
- molding
- electrical testing
- OSP
- surface treatment
- final inspection
In addition, more and more manufacturers are now choosing the manufacturing process of drilling before molding. The following is a manufacturing process diagram of single-sided PCBs:
Applications of Single-sided PCB
The end products that use single-sided PCBs mainly include calculators, charging products, LED light boards, FM wireless radios, timers, etc. At the same time, according to different technology types.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Single-sided PCB
Advantages
- Require less material and have lower cost;
- Require fewer manufacturing processes, resulting in shorter overall production time;
- Simple circuit design and construction, so it does not require extensive professional experience to complete the design
- For large-volume orders, the larger the order quantity, the more favorable the price due to the simple process
Disadvantages
- The limitation of single-side area cannot meet the needs of installing a large number of components and more wiring.
- If it carries too many components, it may cause slow connection speed and power loss, so the application field of the product is very limited.
Single-sided Vs Double-sided PCBs
There’re many difference between single sided and double side PCBs, table below is about the details of their key features.
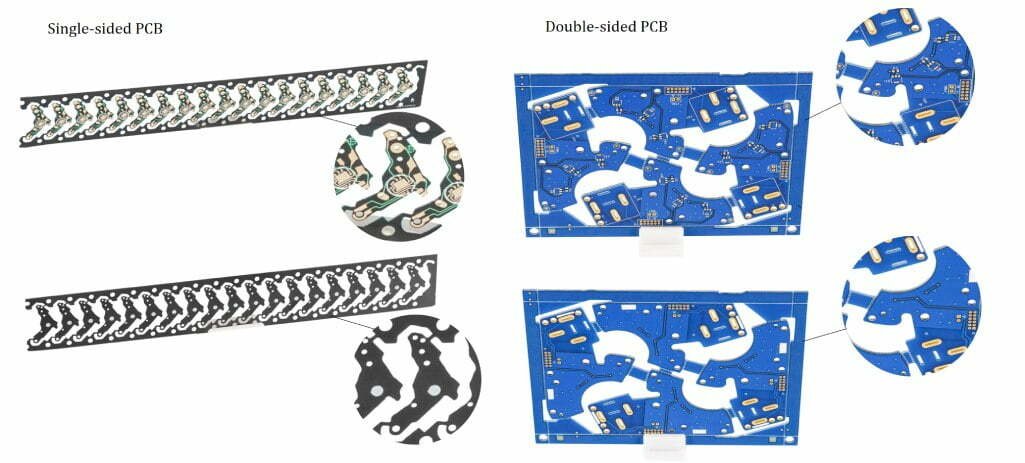
| Features | Single-Sided PCB | Double-Sided PCB |
|---|---|---|
| Copper Foil Distribution | One side only | Distributed on both sides |
| Distribution of Components | Distributed on one side only | Can be distributed on both sides |
| Soldering | Can only be soldered on one side | Can be soldered on both sides |
| Insertion of Components | Components can only be inserted on one side | Components can be inserted on both sides |
| Connections | Connections can only be made on one side | Connections can be made on both sides |
| Space | Requires more space for component layout | Can accommodate more components in the same size |
| Manufacturing Process | Relatively simple | Requires more processing steps and tools |
| Note: Double-sided PCBs typically require through-hole vias for connections. | ||