Pattern Sewing Machine Definition
A pattern sewing machine is a type of sewing machine used to create clothing and other items of a more intricate nature. It is designed to sew a variety of fabrics with a variety of stitches and patterns. It is capable of creating buttonholes, decorative stitches, and embroidery, as well as zippers, seams, and hems.
Pattern Sewing Machine Product
This sewing machine comes with computerized features, which makes it easier to operate. This machine can be connected to a computer to transfer designs from software to the machine. It has a large LCD screen that makes it easy to view the settings. It has an easy to load drop-in bobbin that prevents tangling of threads. The sewing machine also has an easy load drop in bobbin that prevents tangling of threads and a built-in thread cutter for convenience.
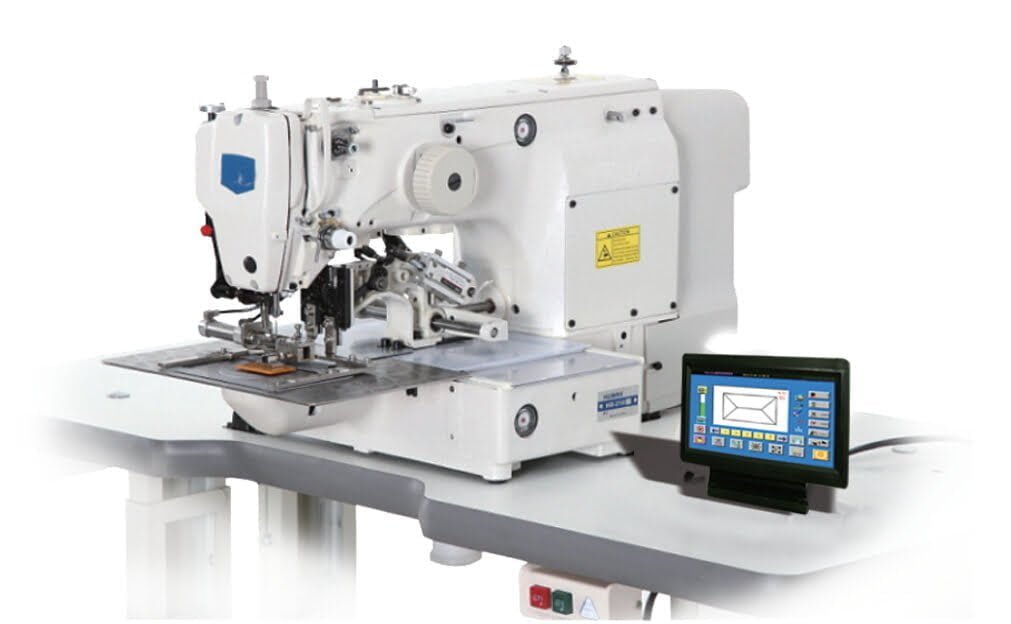

Features
Combined sewing function
The electronic pattern machine realizes the function of sewing multiple patterns on different templates at the same time. When entering the combined sewing mode, the machine will automatically go to the starting point of the next pattern after sewing the first pattern, and wait for the user’s instruction to confirm. to sew.
Quick change mold
The large presser foot frame can be replaced by removing 2 screws, and there is a positioning pin on the large presser foot frame for easy and precise positioning.
Color touch screen
Easily create sewing patterns based on icons and commands, and quickly move them left and right and rotate them clockwise and counterclockwise. In addition, the touch screen can also display the cumulative number of sewing, the shape of the sewing pattern, the size of the horizontal and vertical directions, etc.
Large storage space
The storage system of the electronic pattern machine can directly input sewing patterns through the USB interface. The biggest advantage of this kind of memory is fast transmission speed and large storage capacity. It can be used in pattern sewing, small part sewing, small pattern and reinforcement sewing and other processes.
Sustainability and the circular economy
As the fashion industry continues to grapple with issues of sustainability, there is growing interest in the use of pattern sewing machines to create clothes that are made to last. By using sustainable fabrics and reducing waste, pattern sewing machines can help to create a more circular economy in fashion.
Spcecification
- Maximum speed: 2300/2700 rpm;
- Voltage range: 180V~250V;
- Sewing machine motor: 750W small AC servo motor;
- Lifting amount of outer presser foot: max. 30mm;
- Memory capacity: up to 40,000 stitches for a single pattern;
- Working environment temperature: 0~50℃;
- Working environment humidity: 30%~95% (no condensation);
- Zoom in/out function: zoom in and zoom out on the X and Y axes, 1~400%;
- Cloth feeding method: intermittent feeding (pulse motor drive) 2-axis drive;
- Automatic thread trimming: presser foot lifter, solenoid valve, electromagnet.
Development Landscape of the Pattern Sewing Machine
Customization and personalization:
With the rise of online marketplaces and custom clothing services, there is a growing demand for pattern sewing machines that can be easily programmed to create unique and personalized garments. This trend is particularly popular among younger consumers who are looking for more individualized fashion options.
Integration with smart home technology:
Many pattern sewing machines are now being designed to integrate with smart home technology, allowing users to control their machines remotely and even program them to start sewing automatically at certain times. This trend is helping to make sewing more accessible and convenient for people with busy lifestyles.
Advancements in machine learning and artificial intelligence:
As machine learning and artificial intelligence technology continues to improve, there is growing potential for pattern sewing machines to become even more sophisticated and efficient. This could lead to new innovations in garment design and production, as well as new opportunities for creativity and experimentation in the fashion industry.