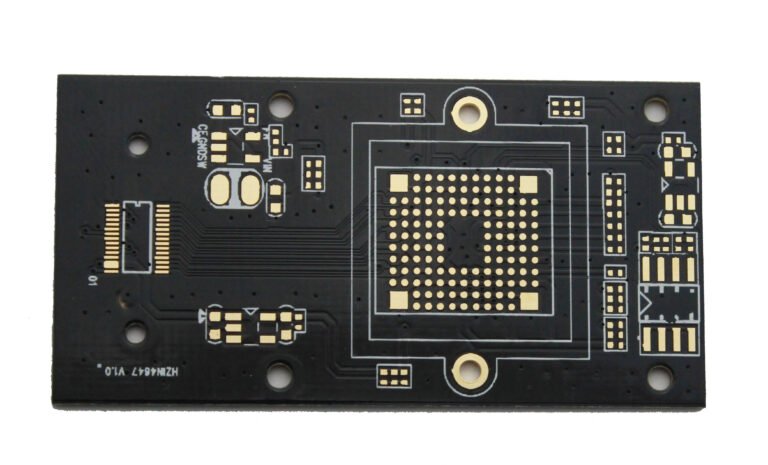
In the realm of electronics manufacturing, printed circuit boards (PCBs) serve as an essential component, connecting electronic elements and enabling efficient functionality. Over the years, the aesthetics and performance characteristics of PCBs have evolved, with black PCBs emerging as a popular choice among designers. Black PCBs, often chosen for their sleek and premium appearance, offer a variety of benefits, particularly in high-end consumer electronics. However, they also present certain challenges that need careful consideration. This article explores the pros and cons of copper black PCBs, offering insights into their applications, limitations, and performance attributes.
What is Copper Black PCB?
A Copper Black PCB is a type of printed circuit board (PCB) that uses a black solder mask instead of the more common green or blue solder masks. The solder mask is a layer of polymer applied to the PCB to protect the copper traces and prevent short circuits. In Copper Black PCBs, the dark color of the solder mask gives the board its distinctive appearance, providing a sleek, high-end look that’s especially favored in premium electronic products.
Why Choose Copper Black PCB?
Black PCBs are becoming increasingly popular due to their distinct visual appeal and technical advantages. Their primary feature is the black solder mask, which not only enhances the appearance but also plays a role in the electrical performance and thermal management of the PCB.
Aesthetic Appeal and Premium Design
One of the most noticeable advantages of black PCBs is their aesthetic value. The deep, dark color gives products a sleek and high-end look, making them particularly popular in premium electronics, such as smartphones, gaming consoles, and LED lighting. The dark background enhances the brightness and contrast of LEDs, improving the overall visual impact. This makes black PCBs a favored choice in applications where both function and appearance are crucial.
Thermal Management Benefits
Black PCBs also offer superior thermal management properties. The dark surface of the PCB absorbs heat more effectively than lighter-colored PCBs, which can help dissipate heat in power-intensive applications. This property is especially beneficial in designs where efficient heat distribution is critical, such as in power supplies and high-performance computing devices. However, it’s important to note that while the black surface improves heat absorption, thermal management in PCBs primarily depends on the materials used and the design itself, not just the color.
Improved Soldering Contrast
The high contrast provided by black PCBs makes solder joints and pads more visible. This is advantageous in manufacturing, as it facilitates visual inspections and ensures better soldering accuracy. The clarity of the soldering process can lead to improved product quality, especially in high-precision electronics.
Pros and Cons of Copper Black PCBs
Copper Black PCBs have grown increasingly popular due to their distinct aesthetic appeal, high-end look, and some functional benefits, particularly in specific electronics applications. However, like any technology, they come with both advantages and challenges. Here’s a detailed breakdown:
Pros of Copper Black PCBs
Enhanced Aesthetic Appeal:
- The dark, sleek look of Copper Black PCBs gives a high-end, premium appearance to products. This is especially valuable in consumer electronics where design is a key part of product branding (e.g., smartphones, high-end gaming consoles).
Improved Thermal Management:
- Black surfaces absorb more heat compared to lighter-colored PCBs. The increased absorption helps dissipate heat from components more effectively, which can be advantageous in high-power applications.
- The heat dissipation qualities of black PCBs may improve overall device performance by reducing the risk of overheating, which can damage sensitive electronic components.
Higher Contrast for Visual Inspection:
- The black background makes copper traces and solder joints stand out more clearly, improving the accuracy of visual inspections. This is particularly beneficial for quality control and can help detect soldering issues more easily during production.
Electromagnetic Compatibility (EMC):
- The use of black solder masks in Copper Black PCBs can improve electromagnetic shielding, reducing electromagnetic interference (EMI). This makes them a good choice for high-frequency devices where signal integrity is crucial.
Durability and Protection:
- The black solder mask can provide better protection against environmental factors like moisture and dust. It helps prevent oxidation of the copper traces, which contributes to longer PCB life.
Cons of Copper Black PCBs
Higher Production Costs:
- Copper Black PCBs typically cost more to produce than standard green PCBs. The primary reason is the cost of the black solder mask, which requires a more precise and complicated manufacturing process.
- Additionally, these boards often require more intensive inspection, which can further drive up costs.
Difficulty in Visual Inspection and Debugging:
- While the contrast in black PCBs is beneficial in some cases, the color can also make it harder to detect very fine traces or defects during visual inspections.
- The dark color can make it more challenging to spot minute errors, especially under low lighting conditions or for human inspectors, which may require specialized equipment for more accurate inspections.
Thermal Expansion Issues:
- While black PCBs may aid in heat dissipation, they can also experience higher thermal expansion compared to other colors. If not properly designed, the increased heat absorption can cause expansion issues, potentially compromising the integrity and longevity of the board.
Potential Design Limitations:
- In some cases, the black solder mask may obscure the visibility of circuit traces, making design and routing more challenging. This is especially true if detailed traces need to be clearly visible for design verification.
The Role of Copper and Solder Mask in Black PCBs
At the core of any PCB is the copper layer, which serves as the conductive pathway for electrical signals. Without adequate protection, the copper is highly susceptible to oxidation, which can degrade the electrical performance of the PCB. To prevent this, a solder mask is applied, which protects the copper from oxidation while also isolating areas that require soldering.
The color of the solder mask, whether black, green, or any other hue, does not directly affect the functionality of the PCB, but it does impact its appearance and ease of manufacturing. Black solder masks, while offering a premium look, may make it harder to inspect the intricate copper traces, especially during repairs or modifications. This has led some manufacturers to prefer darker shades of green or brown, which balance visibility with the aesthetic benefits of black.
Copper Black PCBs vs. Traditional Green PCBs
Here’s a comparative analysis of Copper Black PCBs and Traditional Green PCBs to help you understand the key differences between the two. The table below summarizes the main points:
| Aspect | Copper Black PCBs | Traditional Green PCBs |
|---|---|---|
| Aesthetic Appeal | Sleek, premium look. | Basic, traditional look. |
| Thermal Management | Better heat dissipation. | Standard heat dissipation. |
| Cost | More expensive. | Cheaper. |
| Inspection | Harder to inspect visually. | Easy to inspect visually. |
| EMC | Better EMI shielding. | Standard EMI performance. |
| Durability | Better oxidation protection. | Standard protection. |
| Manufacturing Complexity | More complex production. | Easier to manufacture. |
| Market Perception | Premium products. | Mass-market products. |
Black PCBs in High-End Applications
The unique properties of black PCBs make them particularly well-suited for high-end applications, such as in consumer electronics, medical devices, and specialized industrial equipment. For instance, products like smartphones (including the iPhone), gaming consoles, and other luxury electronic items often feature black PCBs. These devices require not only functional PCBs but also high levels of electromagnetic compatibility (EMC) and radio frequency interference (RFI) shielding—areas where black PCBs excel due to their superior material properties.
In addition, black PCBs are often used in optical instruments and camera equipment, where both performance and aesthetic appeal are critical. The use of transparent inks in conjunction with black PCBs allows manufacturers to create products that showcase both the intricate inner workings of the device and its overall design.
Challenges and Limitations of Black PCBs
Despite their advantages, black PCBs also come with certain drawbacks that need to be considered when selecting them for a project.
Higher Manufacturing Costs
The production of black PCBs is generally more expensive compared to traditional green or blue PCBs. This is due to the specialized black solder mask, which requires additional processing steps and materials. The higher cost of production can be a significant factor for manufacturers, especially in mass-market products where cost efficiency is a priority.
Detection and Inspection Challenges
While black PCBs improve the visibility of solder joints, they can make detecting defects in the PCB itself more difficult. The black surface can reflect light during automated optical inspections (AOI), potentially obscuring fine defects like small traces or solder bridges. This challenge requires more advanced inspection techniques, which can add to the production costs and time.
Thermal Expansion Concerns
Black PCBs, due to their higher heat absorption, may experience increased thermal expansion under high temperatures. This could potentially affect the long-term stability and reliability of the PCB, especially in environments with extreme temperature fluctuations. Engineers must take this into account during the design phase to ensure that the PCB maintains its integrity under varying conditions.
FAQ
Q1: Is black PCB color prone to color variations during manufacturing?
A1: No, color variation is not a significant issue with black PCBs.
While it’s true that color differences may occur during the manufacturing process, black PCBs are often less prone to noticeable color variation compared to other colors like red or blue. The color of black is relatively easier to standardize, making it less likely to result in noticeable defects that could affect the PCB’s performance or quality.
Q2: Does black PCB make it harder to detect circuit traces during inspection?
A2: It’s a matter of perspective, but it’s not a significant issue.
It is true that black PCBs can make it harder to distinguish fine circuit traces, especially when compared to lighter-colored PCBs. However, manufacturers typically use circuit diagrams and specialized inspection equipment, such as automated optical inspection (AOI), to detect defects. The color of the PCB does not significantly hinder the debugging or quality control process as long as proper inspection techniques are applied.
Q3: Is black PCB used to prevent product duplication or counterfeiting?
A3: This claim lacks substantial evidence.
While some people may suggest that the use of black PCBs is a strategy to deter counterfeit products, this is not a common industry practice. Black PCBs are typically chosen for their aesthetic value and functional benefits, such as heat absorption and enhanced visual contrast for soldering. The idea of using black PCBs specifically to prevent duplication is not widely accepted or practiced.
Q4: Do black PCBs have better thermal management compared to other colors?
A4: Black does help with heat absorption, but it’s not the primary factor in thermal management.
While black surfaces do absorb heat more effectively than lighter colors, the primary factor affecting thermal management is the PCB’s material composition, design, and thermal vias, not the color of the solder mask. Black PCBs may appear to dissipate heat faster due to their color, but effective thermal management relies on the overall PCB design, including the use of thermal substrates or materials such as aluminum or copper-based boards.
Q5: Are black PCBs more expensive than green PCBs?
A5: Yes, black PCBs generally cost more than green PCBs.
The production of black PCBs involves additional processing steps and specialized materials, which makes them more expensive than the more commonly used green PCBs. Green is the default color for most PCBs, and its production is more cost-effective due to the large volume of demand. In contrast, black PCBs, due to their premium appearance and added complexity, typically incur higher costs.
Q6: Does the color of the PCB impact its electrical performance?
A6: No, the color itself does not affect electrical performance.
The color of the PCB, whether black, green, blue, or any other hue, has no direct impact on the PCB’s electrical conductivity or performance. The electrical properties of the PCB are determined by the materials used in the PCB (e.g., copper) and the design of the circuitry, not the solder mask color. The main purpose of the color is for aesthetic reasons and to aid in manufacturing processes.
Q7: Are black PCBs more difficult to repair or debug due to the color?
A7: No, the color itself does not significantly hinder repair or debugging.
While it’s true that black PCBs can obscure the visibility of the copper traces, this is not a critical issue during repairs. Engineers typically rely on circuit diagrams and electronic testing tools when diagnosing issues, rather than visual inspection alone. Black PCBs may require more attention during the visual inspection phase, but they do not inherently make repairs or debugging more difficult.
Q8: Do black PCBs provide better protection against oxidation compared to other colors?
A8: No, oxidation resistance is not directly influenced by color.
The ability of a PCB to resist oxidation is primarily determined by the protective solder mask and the copper plating, not by the color of the solder mask. Black PCBs do not offer superior oxidation protection compared to green or other colored PCBs. The primary role of the solder mask, regardless of color, is to protect the copper traces from environmental factors like moisture and air that can lead to oxidation.
Q9: Can black PCBs enhance product quality and reliability?
A9: Black PCBs may improve certain aspects of product appearance and heat management, but they are not inherently more reliable.
The appearance of black PCBs can certainly contribute to a product’s high-end image, especially in consumer electronics. However, reliability is primarily determined by the PCB’s design, materials, and manufacturing quality, rather than its color. Black PCBs may have some advantages in heat absorption and visual contrast for soldering, but these do not directly translate to improved overall reliability.
Conclusion
Black PCBs, with their combination of aesthetic appeal and technical advantages, have become a prominent choice in the design of high-end electronic devices. Their ability to enhance product appearance, improve thermal management, and aid in precise soldering makes them ideal for use in advanced technology applications. However, manufacturers must carefully consider the higher production costs, potential inspection difficulties, and thermal expansion issues associated with black PCBs.
In the evolving world of electronics, black PCBs represent a perfect balance between function and form, allowing designers to meet both performance and aesthetic requirements. As technology continues to advance, the role of black PCBs in the future of electronics manufacturing is likely to grow, offering even more opportunities for innovation and high-quality design.