
RF Circuits Explained: Basics & Working Principles
New to RF? Understand radio frequency circuits: components, impedance matching, and signal propagation. Applications in wireless devices. Beginner’s guide inside!
Schematic & Gerber restoration
MCU/CPLD code restore access & backup
1:1 exact hardware replication
BLE & Classic BT wireless solutions
Precision PID & thermal management
High-efficiency motor drive control
Industrial RS485/RTU communication
Custom STM32/ESP32 firmware & HW
Calculate the PCB trace width based on temperature rise, current, and copper thickness (IPC-2152).
Signal processing is the manipulation of signals to extract valuable information or optimize their performance. This category covers various signal processing techniques used in electronics, from analog to digital signal processing (DSP). You’ll find articles on filtering, noise reduction, and techniques for improving signal quality in PCB designs. Learn how to apply these techniques to enhance communication circuits, sensors, and other electronic systems.

New to RF? Understand radio frequency circuits: components, impedance matching, and signal propagation. Applications in wireless devices. Beginner’s guide inside!
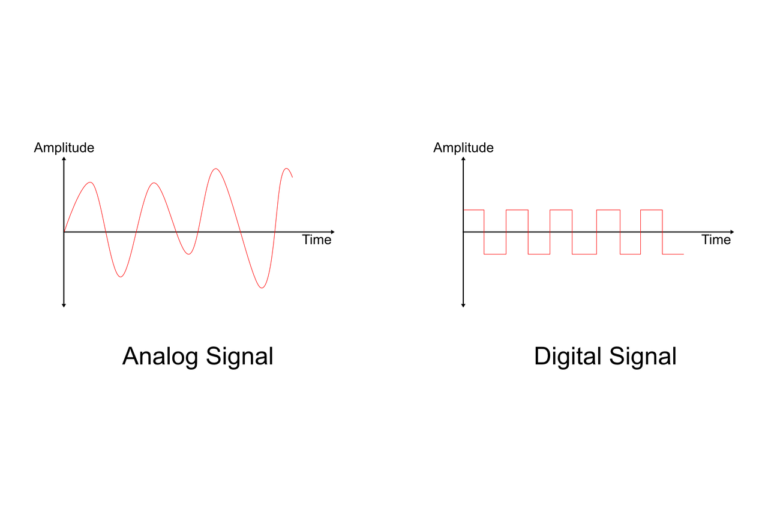
When you tune the radio in your car or home, you are listening to different types of signals. You may not think about it much, but both analog and digital signals play an important role in our everyday life. Analog
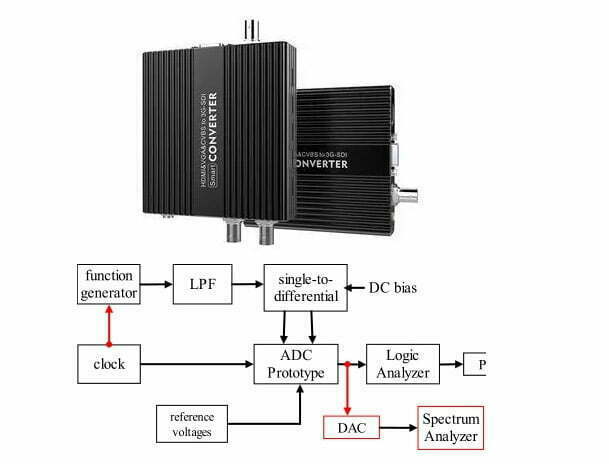
Among smart instruments, ADC and DAC converters play a pivotal role. We know that currently widely used microprocessors can only deal with discrete digital signals. There is no way to feed a continuous analog signal from the physical world into

Understand crosstalk: signal interference, trace spacing, and grounding solutions. Tips for high-speed designs to minimize noise. Essential for signal integrity!
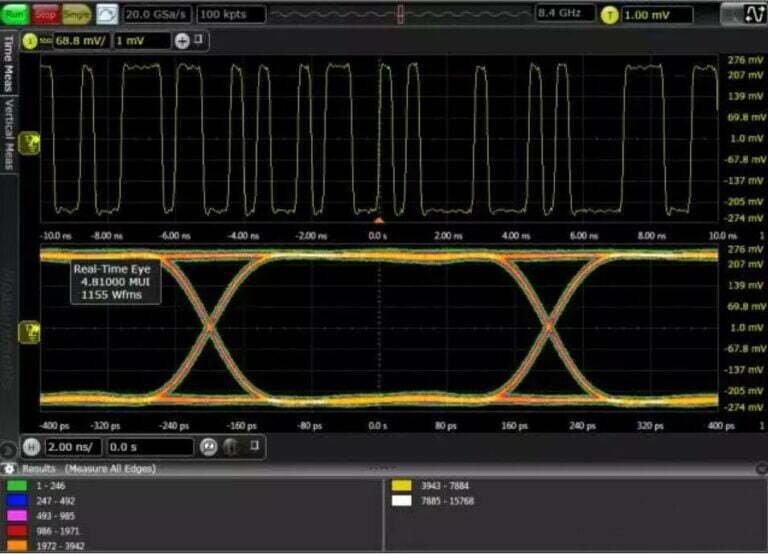
Master SI issues: reflections, crosstalk, and impedance control. Tips for routing, termination, and simulation tools like HyperLynx. Critical for high-speed designs!
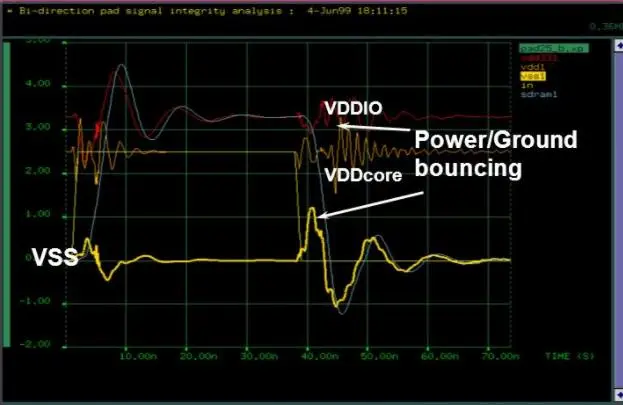
LVDS basics: differential signaling, data rates, and noise immunity. Learn to route LVDS traces in high-speed PCBs. Applications in displays/networking. Guide inside!
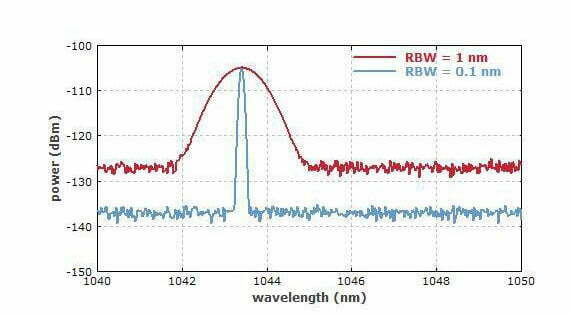
What is signal to noise ratio? The signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) is a measure used in science and engineering that compares the level of a desired signal to the level of background noise. It is defined as the ratio of signal

DSP basics: architectures, applications in audio/video processing, and real-time computing. Compare TI/ADI DSPs for your design. Expert insights inside!
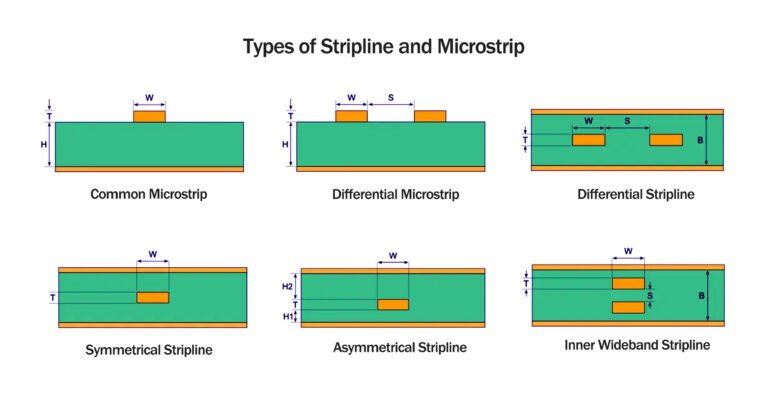
Explore the critical differences between stripline and microstrip with practical examples in 5G infrastructure, data centers, and medical devices. Optimize signal integrity for high-frequency PCB design.