When you tune the radio in your car or home, you are listening to different types of signals. You may not think about it much, but both analog and digital signals play an important role in our everyday life. Analog and digital signals are two broad classes of signals that can be used to transmit information. They have different properties and are used for different applications. Both types come with their advantages and disadvantages. In this blog post, we’ll go over some basic information about analog and digital signals as well as how they are used. Let’s dive in!
What is an Analog Signal?
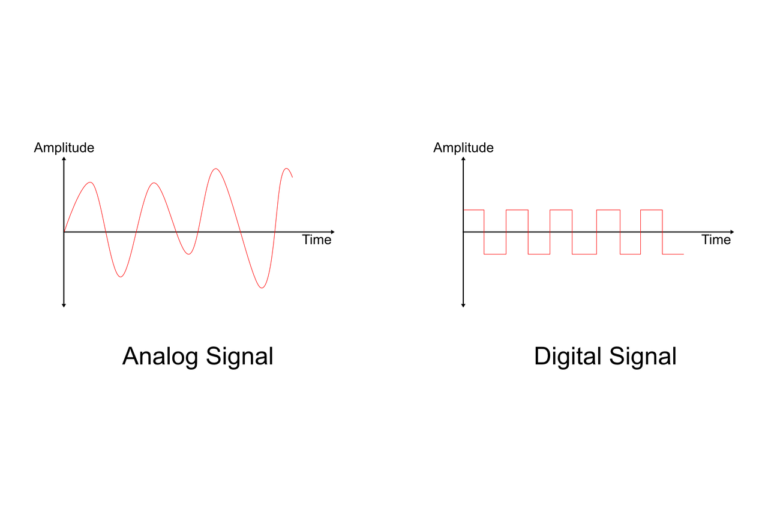
Analog signals are one of the two broad classes of signals. They are also referred to as continuous signals because they have a continuously varying value. This means that their value can change endlessly within a given range. In other words, an analog signal has a continuously changing voltage or current. Analog signals are commonly used to represent things in nature that change over time, such as sound, images, and temperature. For example, the sound coming out of your speakers is an analog signal. The brightness and the colors of an image are also analog signals. Temperature is a good example of how signals can be quantized. Different temperatures can be measured using different voltages that can be understood by a computer.

What is a Digital Signal?
A digital signal, on the other hand, is a discrete signal. It changes its state as it moves between different levels. A digital signal is either at a high or low level, which means that it has been quantized. A digital signal is binary, which means it consists of only 0s and 1s. Digital signals are used to transmit discrete information, such as computer data. They can only exist at either one of two levels. Digital signals have higher noise immunity than analog signals. This means that they are less affected by interference. Digital signals are also easier to process, store and transmit compared to analog signals.

The Difference Between Analog and Digital Signals
Analog and digital signals are different in terms of both their accuracy and their ability to represent information. Let’s look at each in more detail.
Accuracy: Analog signals are continuous and can represent any value within a given range. This means that they are infinitely accurate. A digital signal is discrete, which means that it can only represent certain values within a given range. This means that digital signals are only finitely accurate.
Information: Analog signals are continuous, which means they can represent both analog and digital information. Digital signals are discrete, which means that they can only represent digital information.
Pros and Cons of Analog Signals
Pros of analog signals:
- Analog signals are continuous and can represent any value within a given range. This means that they are infinitely accurate and can represent both analog and digital information.
Cons of analog signals:
- As a disadvantage, analog signals are susceptible to noise and interference, and therefore have limited range.
Pros and Cons of Digital Signals
Pros of digital signals:
- They are finitely accurate but have a high noise immunity.
- Digital signals have reduced distortion compared to analog signals.
- Digital signals are also suitable for long-distance transmission because it has a smaller bandwidth requirement than analog signals.
Cons of digital signals:
- Digital signals are discrete, which means that they can only represent digital information.
How are Analog and Digital Signals Used?
Analog signals are used to transmit audio, visual, and temperature information. Examples include the radio waves used to transmit music, the light used to transmit images in a movie theater, and thermometers used in laboratories.
Digital signals are used to transmit information such as computer data. Examples include Ethernet cables used to connect computers in a network and fiber-optic cables used to transmit telephone calls.
Digital-to-Analog Conversion
Digital signals are usually first converted into analog signals using an digital-to-analog converter (DAC). This is necessary because humans can only understand and process analog signals. An DAC converts the discrete levels of digital signals into continuous analog signals so that they can be understood. A DAC is a device used to convert analog signals into discrete digital signals. This is done so that the information can be stored on a computer or stored on a computer for later transmission. (Click here to see how DAC and ADC converters work)

FAQs
There is no clear answer as to which type of signal is better. Each has its own advantages and disadvantages. Analog signals are typically easier to work with and provide more information than digital signals. However, digital signals are more precise and can be more easily processed by computers.
Analog signals are typically continuous, meaning that they vary smoothly over time. Common examples of analog signals include things like audio signals (sounds), video signals (images), and sensor readings (temperature, pressure, etc.).
Digital signals, on the other hand, are typically discrete, meaning that they take on a finite number of values. Common examples of digital signals include things like computer data (1s and 0s), digital audio and video (compressed into a finite number of bits), and digital sensor readings (also compressed into a finite number of bits).
Yes, there is a noticeable difference between analog and digital audio. Analog audio has a warm, natural sound, while digital audio is more clean and precise. However, both types of audio can be excellent quality, depending on the recording and playback equipment used.
Computers use digital signals for a variety of reasons. One reason is that digital signals are more precise than analog signals. This means that digital signals can be processed more quickly and accurately by computers. Another reason is that digital signals are less susceptible to noise and interference than analog signals. This means that digital signals can be transmitted over longer distances with less signal degradation.
Analog and digital signals are used in automation to control various devices and processes. Analog signals are typically used to control devices that require a continuous or variable input, such as motors and valves. Digital signals, on the other hand, are typically used to control devices that require a discrete or ON/OFF input, such as switches and relays.
Final Words
When it comes to signals, it is important to understand the difference between analog and digital. Analog signals are continuous and can represent any value within a given range. Digital signals are discrete and can only represent two values. These two broad classes of signals can be used to transmit information. They have different properties and are used for different applications. Both types come with their advantages and disadvantages. In this blog post, we’ve gone over some basic information about analog and digital signals as well as how they are used.