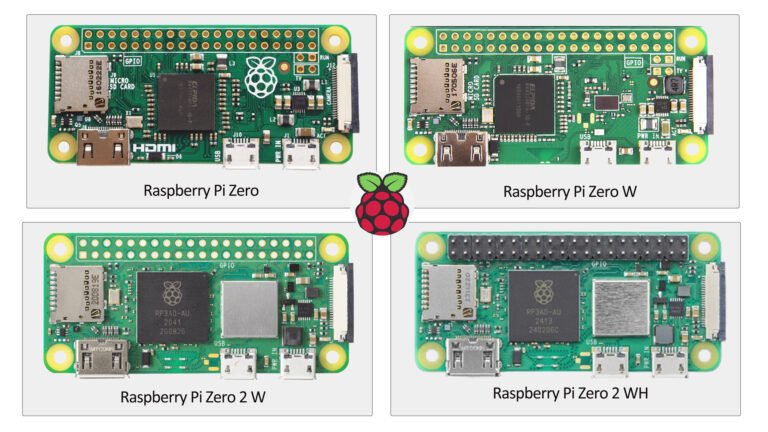
The Raspberry Pi Zero series is widely used in various embedded and DIY projects. As the low-cost variant of the Raspberry Pi, the Zero series offers powerful features while maintaining a compact size and affordable price. Over time, these boards have gradually evolved with improved performance and additional features. In this article, we will delve into the key differences between the Raspberry Pi Zero, Zero W, Zero 2 W, and Zero 2 WH, helping readers understand which version is most suitable for their needs.
Raspberry Pi Zero
The Raspberry Pi Zero is the smallest and cheapest single-board computer released by the Raspberry Pi Foundation, first introduced in 2015. Its main appeal lies in its compact size and extremely low cost, making it ideal for embedded projects, IoT devices, and educational purposes.

Specifications
- Processor: Broadcom BCM2835 1GHz ARM11 (40% faster than Raspberry Pi 1)
- Memory: 512MB LPDDR2 SDRAM
- Storage: micro-SD card slot
- Video Output: Mini-HDMI port, supports 1080p 60Hz video
- Ports: 1 Micro-USB port for data transfer, 1 Micro-USB port for power
- GPIO: 40-pin GPIO (requires soldering)
- Dimensions: 65mm x 30mm x 5mm
Pros and Cons
- Pros: Extremely small, very affordable, suitable for basic projects.
- Cons: Single-core processor with limited performance, not suitable for heavy workloads.
Use Cases
- Small embedded projects
- Basic IoT devices
- Educational tools for learning programming
Raspberry Pi Zero W
The Raspberry Pi Zero W builds upon the original Zero with added wireless functionality (Wi-Fi and Bluetooth) and was released in 2017. The inclusion of wireless capabilities makes it an even more attractive option for IoT projects while maintaining a low price.

Specifications
Processor: 1GHz, single-core CPU
Memory: 512MB RAM
Storage: micro-SD card slot
Video Output: Mini-HDMI port
Ports: Micro-USB OTG port, Micro-USB power port
Wireless: 802.11n Wi-Fi, Bluetooth 4.0
GPIO: 40-pin (soldering required)
Camera Interface: CSI camera ribbon cable interface
Pros and Cons
- Pros: Adds Wi-Fi and Bluetooth support, suitable for IoT applications.
- Cons: Processor performance is still relatively weak, suitable for low-load tasks.
Use Cases
- IoT applications
- Wireless sensor devices
- Home automation systems
Raspberry Pi Zero 2 W
The Raspberry Pi Zero 2 W, released in 2021, uses the BCM2710A1 SoC from the Raspberry Pi 3, significantly improving performance, particularly in multi-threaded workloads. While it still maintains the small size and low price of the Zero series, the performance boost allows it to handle more complex tasks.

Specifications
- Processor: Broadcom BCM2710A1, quad-core 64-bit ARM Cortex-A53 @ 1GHz
- Memory: 512MB LPDDR2 SDRAM
- Wireless: 2.4GHz IEEE 802.11b/g/n Wi-Fi, Bluetooth 4.2
- Ports: 1 USB 2.0 port with OTG, Mini-HDMI port, 40-pin GPIO, CSI camera interface
- Video Decode: H.264, MPEG-4 decode (1080p30)
- Dimensions: 65mm x 30mm x 5mm
Pros and Cons
- Pros: Significant performance increase, supports more demanding applications, backward compatibility with accessories.
- Cons: Slightly more expensive than the Zero W.
Use Cases
- Multi-tasking applications
- Embedded devices with wireless connectivity
- Video playback applications
Raspberry Pi Zero 2 WH
The Raspberry Pi Zero 2 WH is similar to the Zero 2 W but comes with an important enhancement: pre-soldered 40-pin GPIO headers. This makes it easier for developers to quickly connect external hardware, offering greater flexibility and expansion possibilities, particularly useful for IoT and home automation projects.

Specifications
- Processor: Broadcom BCM2710A1, quad-core 64-bit ARM Cortex-A53 @ 1GHz
- Memory: 512MB LPDDR2 SDRAM
- Wireless: 2.4GHz Wi-Fi, Bluetooth 4.2
- Ports: Mini-HDMI, Micro-USB 2.0, 40-pin GPIO, CSI camera interface
- Dimensions: 65mm x 30mm x 5mm
Pros and Cons
- Pros: Pre-soldered 40-pin GPIO header, convenient for hardware connections.
- Cons: Slightly more expensive than the Zero 2 W.
Use Cases
- Highly customizable projects
- IoT devices
- Home automation and sensor networks
Comparision of Raspberry Pi Zero Series Boards
| Feature | Pi Zero | Pi Zero W | Pi Zero 2 W | Pi Zero 2 WH |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Processor | Broadcom BCM2835 1GHz ARM11 | Broadcom BCM2835 1GHz ARM11 | Broadcom BCM2710A1 1GHz Cortex-A53 | Broadcom BCM2710A1 1GHz Cortex-A53 |
| Memory | 512MB LPDDR2 SDRAM | 512MB LPDDR2 SDRAM | 512MB LPDDR2 SDRAM | 512MB LPDDR2 SDRAM |
| Wireless | No | 802.11n Wi-Fi, Bluetooth 4.0 | 802.11b/g/n Wi-Fi, Bluetooth 4.2 | 802.11b/g/n Wi-Fi, Bluetooth 4.2 |
| GPIO | 40-pin, requires soldering | 40-pin, requires soldering | 40-pin, requires soldering | 40-pin, pre-soldered |
| USB Ports | 1 Micro-USB | 1 Micro-USB, OTG | 1 USB 2.0, OTG | 1 USB 2.0, OTG |
| Camera Interface | No | CSI camera interface | CSI camera interface | CSI camera interface |
| Video Output | Mini-HDMI | Mini-HDMI | Mini-HDMI | Mini-HDMI |
| Price | $5 | $15 | $15 | $18 |
| Use Cases | Basic embedded projects | IoT, sensor devices | Multi-tasking applications | IoT, hardware connections |
Conclusion
By comparing the Raspberry Pi Zero series, we can see the significant differences between each version, especially in terms of performance, wireless features, and GPIO ease of use. If your project requires wireless connectivity and higher performance, the Zero 2 W and Zero 2 WH are better options. For simpler, budget-conscious applications, the Zero and Zero W are still great choices. Selecting the right model based on your specific needs will enhance both your project development and the overall experience.