There are many uses for PCB transformers in power supply circuits, and they provide impedance matching. They are compact, lightweight and customizable. Additionally, they can reduce noise and boost signal strength. However, selecting the right pcb transformer is crucial to achieving the best results.
There are different types of PCB transformers available based on their design and the type of core material they use. Before you buy one, there are a few things that you need to keep in mind. This article explains everything you need to know about these useful devices before making your purchase decision.
What is a PCB Transformer?
A Printed Circuit Board (PCB) transformer is a tiny, plug-in transformer that provides extra voltage or current to a component. It is installed on the PCB to provide extra voltage or current. It has a bobbin, iron core and a winding. These devices can reduce the noise in an electrical circuit, and increase signal strength and impedance matching.
Types of PCB Transformers
There are different types of PCB transformers available based on their design and the type of core material they use.
Single-phase transformer: A single-phase transformer contains two primary windings. One of the windings is center-tapped while the other is end-tapped. They are available in different types such as delta, star, wye, etc. A delta transformer has two secondary windings and a star transformer has a single secondary winding.
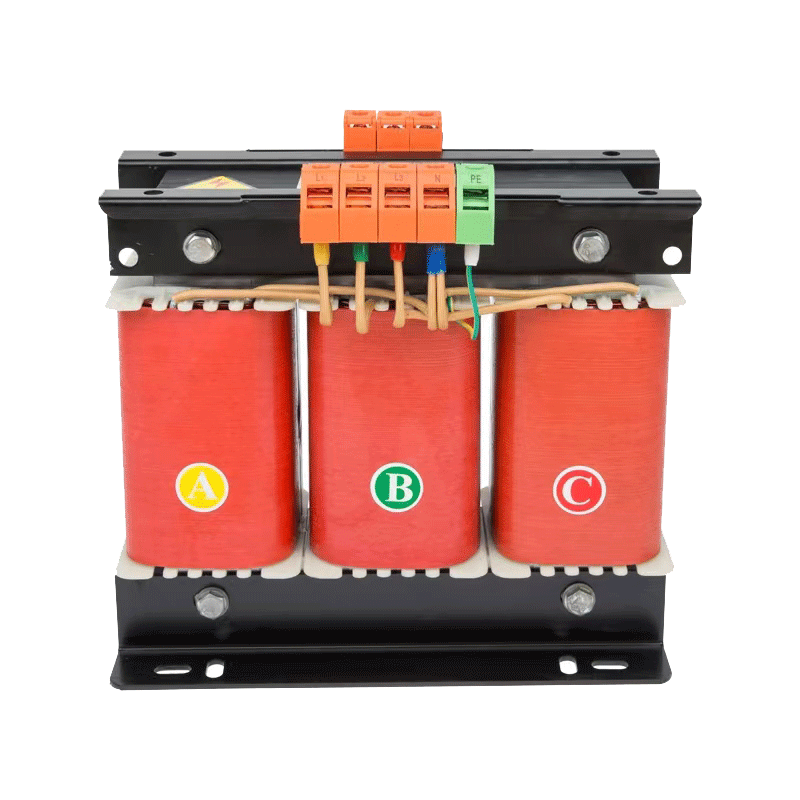
Three-phase transformer: They have three primary windings and two secondary windings. They are available in different types such as wye, wye-delta, delta-delta, delta-wye, and wye-wye.
How do pcb transformer work?
When a voltage is applied to a transformer, the mutual induction produces an electromagnet around the transformer core. The core plays a role of both electric and magnetic field in mutual induction.

The primary coil and the secondary coil are connected in parallel across the supply. So that at all times, the voltage between them is fixed. An induced voltage occurs between the coils when current flows through the primary coil and the secondary coil.
When a magnetic material’s properties undergo an induced change in permeability, a voltage is generated in the windings and hence in a load connected to them. The current through the wire creates an electromotive force (EMF), which opposes the change of field strength (Br).
The material for the core of PCB transformer
The core of the PCB transformer is made of iron or steel. The type of core depends on the application and voltage rating of the transformer. Transformers are available in different types of cores based on their application and voltage rating.
– Iron core: Iron core PCB transformers are useful for applications that require a high current and low-voltage circuits. They are also suitable for applications where there is significant variation in the load current.
– Steel core: Steel core PCB transformers are suitable for high-voltage circuits as well as high-power applications.
Commutator and interrupter types of PCB transformers
Commutator transformers are mainly used in industrial applications. They are best choice for single-phase and three-phase applications. These transformers have two windings and a single common terminal. They have one winding that makes it easy to connect the transformer and two terminals.
Interrupter transformers are mainly used in commercial applications. They are low in cost and are suitable for single-phase applications. These PCB transformers are suitable for applications that have a consistent load current.
How to select the right PCB transformer?
There are a few things you need to keep in mind before you buy a PCB transformer. The different factors include voltage rating, current rating, type of core, type of winding, etc.
Voltage rating – The voltage rating of a PCB transformer indicates the maximum voltage that can be applied across its terminals. Transformers are available for different voltage ratings.
Current rating – The current rating of a PCB transformer indicates the maximum current that it can safely handle. Transformers are available for different current ratings.
Type of core – Transformers are available in different types of cores based on their application and voltage rating.
Type of winding – Transformers are available in single and three-phase windings.
Summary
When designing any type of electronics, it’s important to take into account the various factors that could have an impact on its performance. Among these elements, you will find:
There are many different types of PCB Transformers available in the market today. Each of these has its own advantages and disadvantages. To help you choose the right one for your specific needs, we hope this article will be helpful for you.








