What is Reflow Soldering?
This section lays the groundwork by explaining the fundamental "what," "why," and future of reflow soldering in modern electronics manufacturing. It also highlights its widespread applications.
Reflow soldering is a fundamental technique that creates electrical and mechanical connections between electronic components and a printed circuit board (PCB) by heating a pre-applied solder paste to reflow (melt and re-solidify). This process is crucial for producing the high-density, miniaturized devices we use every day.
Why It's Important
It enables the mass production of devices like smartphones, laptops, and wearables. Its ability to create reliable solder joints is essential across a wide range of industries.
Key Industry Applications
Reflow soldering is vital in consumer electronics, automotive electronics, aerospace and defense, and medical devices, where reliability is the top priority.
The Future of Reflow
The field is constantly evolving. Future advancements include more intelligent equipment, new solder materials, and the integration of 3D printing and AI/ML to further enhance the quality, efficiency, and flexibility of manufacturing.
The Process Flow: From Paste to Joint
This section guides you through each step of the reflow soldering process. Use the interactive flowchart and temperature profile chart to understand the key parameters and goals of each stage.
Process Flow
Step 1: Solder Paste Printing
Precisely apply solder paste to PCB pads.
Step 2: Component Placement
Automated machines place components on the paste.
Step 3: Reflow Soldering
The PCB assembly passes through the reflow oven.
Solder Paste Printing
This is the critical first step for a high-quality solder joint. A thin sheet of metal, a stencil, with openings matching the PCB pads is used. Solder paste is then pushed through these openings onto the pads. The amount and position of the paste must be precisely controlled to prevent defects.
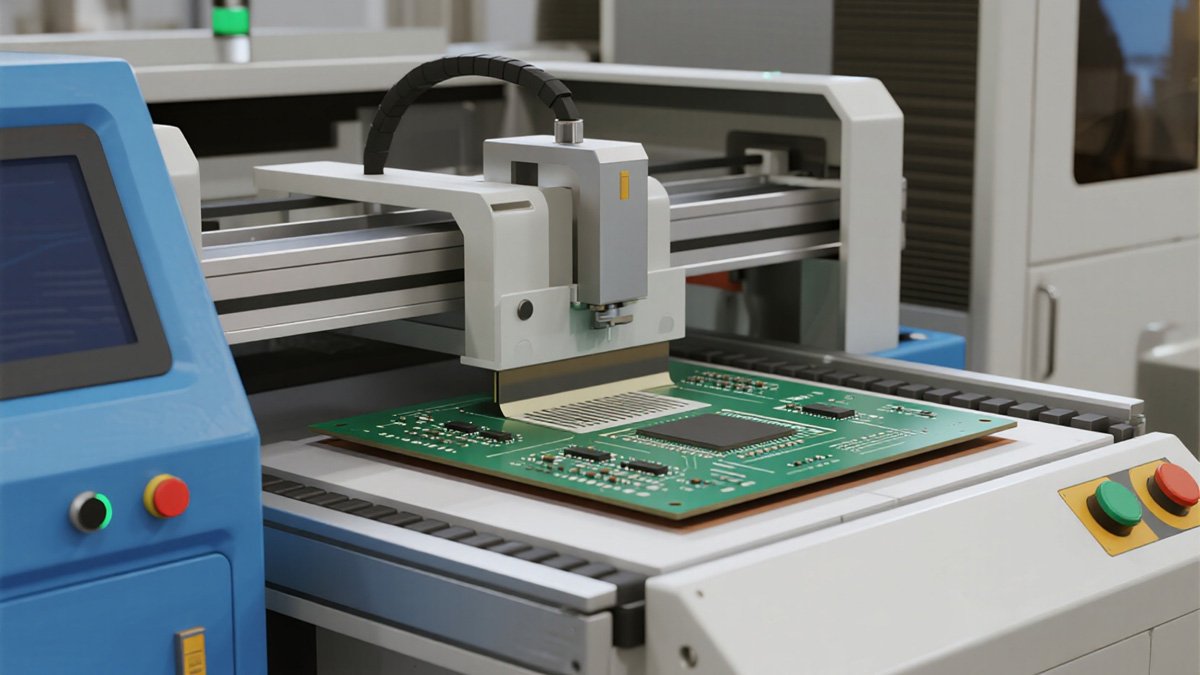

Component Placement
After the paste is printed, high-speed pick-and-place machines pick up thousands of tiny components from feeders and place them precisely on top of the solder paste using vision systems. The paste's stickiness holds the components in place temporarily before soldering.
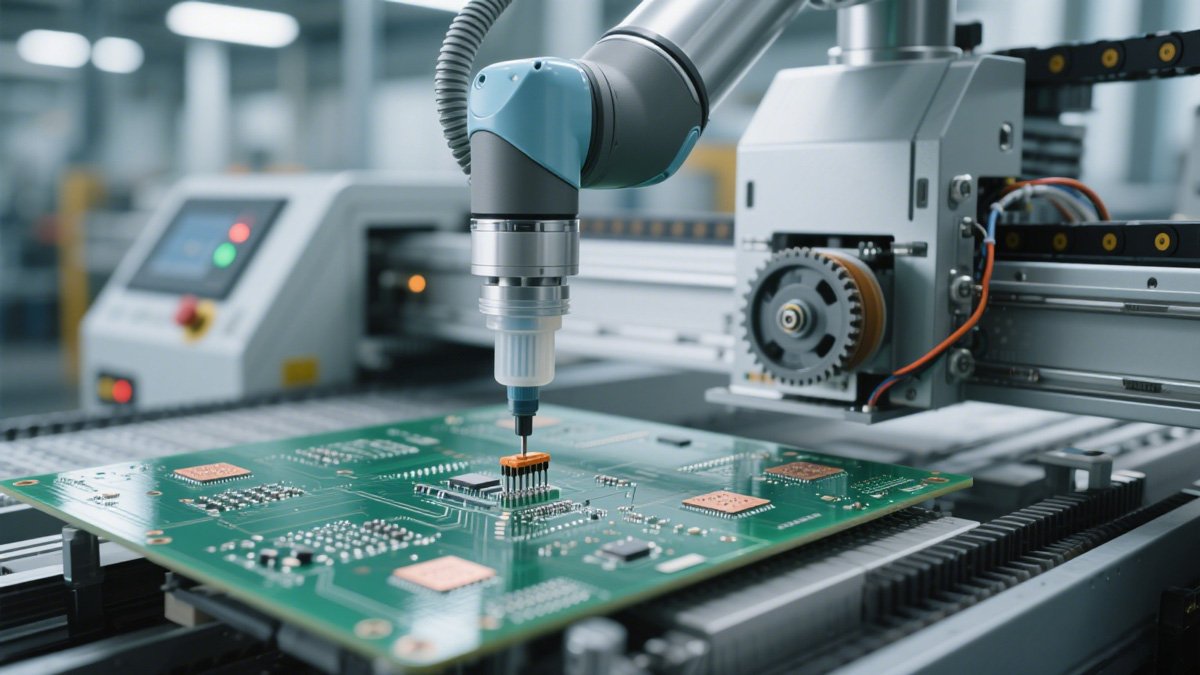
Reflow Soldering
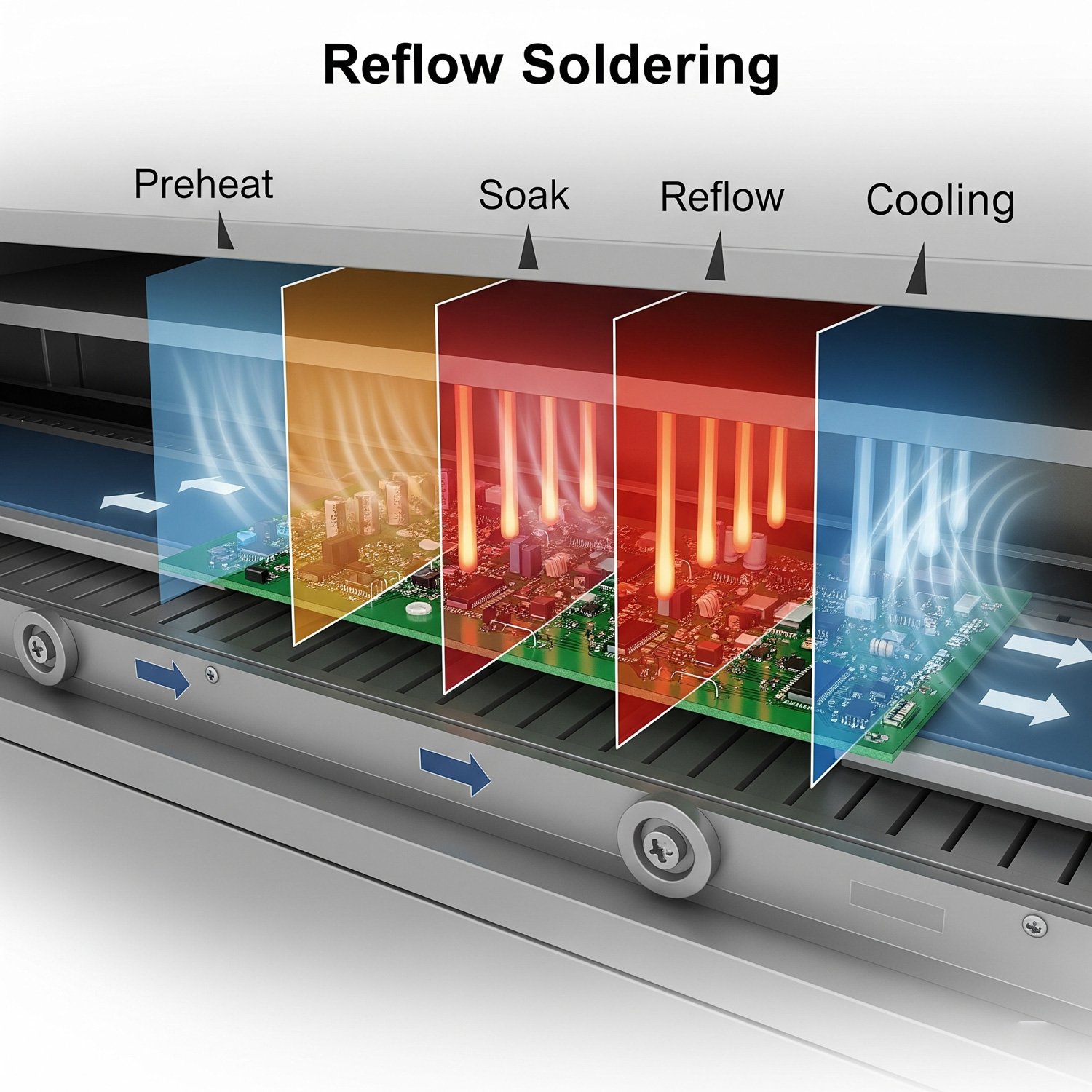
This is the core of the process. The assembled PCB enters a long reflow oven with multiple temperature zones. As it moves along the conveyor belt, it follows a carefully controlled heating, soaking, reflow, and cooling process, known as the "temperature profile," which completes the soldering.
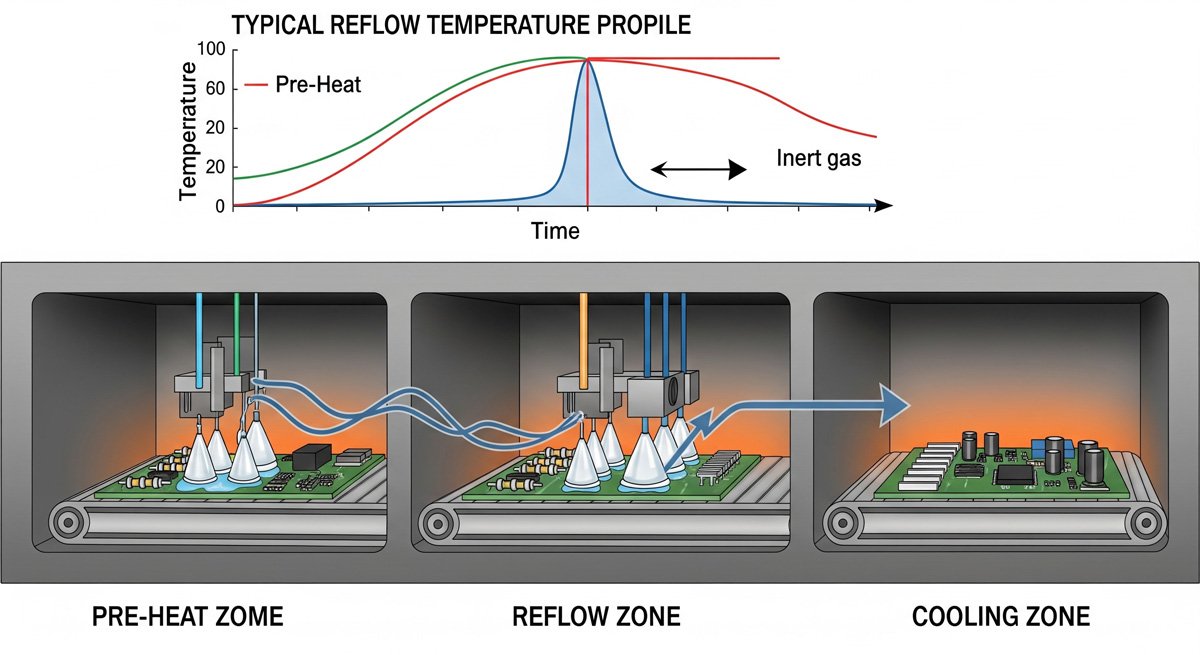
Interactive Temperature Profile
Click a button to see stage details
The temperature profile is the heart of the reflow process, precisely controlling the chemical and physical changes that occur during soldering.
Common Defects and Solutions
Even in highly automated processes, issues can arise. This section is a practical guide to help you quickly identify the root causes of common soldering defects and find effective solutions to improve product quality.
Reflow Soldering vs. Wave Soldering
Reflow is not the only technique. Comparing it to wave soldering helps you understand their fundamental principles, advantages, and applications, leading to more informed technical decisions.
| Feature | Reflow Soldering | Wave Soldering |
|---|---|---|
| Component Type | Surface Mount Components (SMT) | Through-Hole Components (THT) |
| Process Principle | Heating a pre-applied solder paste | PCB passes over a wave of molten solder |
| Accuracy | Very high, suitable for high-density components | Lower, not suitable for high-density assemblies |
| Primary Application | Smartphones, laptops, wearables (consumer electronics) | Power supplies, industrial control boards, home appliances |
Frequently Asked Questions
This section provides concise answers to common questions about reflow soldering, perfect for a quick review or clarifying core concepts.