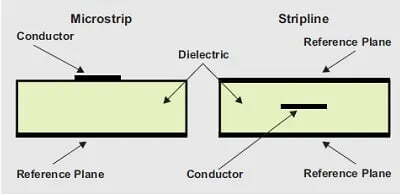
PCB dielectric materials are an essential part of any electronics project. They provide insulation, protection, and support for components in a circuit board. This ensures that your components won’t short out or be damaged due to excessive heat or vibration. With the right dielectric material, you can create a reliable and long-lasting circuit board that is resistant to all sorts of environmental conditions.
What is PCB Dielectric Materials?
PCB dielectric materials are the insulating layers between the copper layers of a printed circuit board (PCB). These materials are usually made of a polyimide or polyester laminate and provide electrical isolation between the traces and components on the board. They also help dissipate heat generated by high-power components such as microprocessors.
Benefits of Using PCB Dielectric Materials
PCB dielectric materials play an important role in the design and manufacture of printed circuit boards (PCBs). PCB dielectrics are used to insulate conductive layers and provide reliable electrical connections while helping to reduce unwanted electrical interference. The use of dielectric materials offers a number of advantages, including improved signal integrity, increased circuit densities, increased power dissipation capability, reduced crosstalk, improved noise immunity, and reduced cost.
improve signal integrity
The dielectric material helps to separate and route signals between different layers and minimizes crosstalk between adjacent traces. This improves signal integrity, reduces EMI, and improves the overall performance of the circuit board. Dielectric materials are available in a variety of formulations and can be tailored to meet specific application requirements. For example, high dielectric constant materials provide improved signal transmission characteristics, while low dielectric constant materials can reduce signal propagation delays and improve signal integrity. Low-loss dielectric materials can also minimize signal loss and improve signal integrity.
Reduce Board Size
The use of PCB dielectrics can also reduce the number of layers required in a circuit board and enable higher densities. These materials are lightweight and easy to integrate into the design, which allows for smaller and more compact designs. Furthermore, their low cost makes them an attractive option for many PCB applications.
Protect PCB components
Dielectric materials are also used to protect components by providing a barrier against environmental contaminants. By providing a layer between the PCB and the environment, these materials can help to prevent corrosion and other damage that could adversely affect the reliability and performance of the circuit board.
help to dissipate heat
In addition, PCB dielectrics help to dissipate heat generated by components, thus increasing the overall reliability of the board. This can be especially important for high-power applications which generate more heat than lower-power devices. Dielectric materials also help to reduce the size of the board by reducing the need for additional layers. In turn, this can reduce material costs and improve design flexibility.
Overall, the use of PCB dielectric materials can provide significant benefits to printed circuit board manufacturers and designers.
Types of PCB Dielectric Materials
PCB dielectric materials are used for insulation, construction and protection of electrical components. These materials come in a variety of forms, including rigid, flexible and metal-backed laminates. The most commonly used PCB dielectric materials include:
Polyimide
Polyimide is a highly heat-resistant material that is often used in high temperature applications. It is also very durable and provides excellent insulation properties.
Polyester
Polyester is a synthetic resin material commonly used in PCBs due to its low water absorption, low CTE and good electrical properties. It is suitable for applications that require high dimensional stability and good electrical insulation.
FR-4
FR-4 is a type of epoxy glass composite that is used in many electronic devices. It is resistant to environmental elements such as moisture and chemicals.
Epoxy
Epoxy is a popular choice for PCBs due to its durability and low cost. It is also an excellent electrical insulator and has good adhesion properties.
polyethylene terephthalate (PET)
PET has good mechanical strength and is highly resistant to chemicals. It is frequently used in combination with other materials to provide improved performance and reliability. Polyester is a very cost-effective material that is commonly used for single-sided PCBs. It has good thermal properties, low moisture absorption, and good dielectric properties.
Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE)
PTFE is a highly durable and non-sticky material that is often used in the manufacturing of circuit boards. It is also strong and provides superior insulation.
Ceramic
Ceramics are used for their insulation and thermal properties. They are also resistant to chemicals and have high electrical resistance.
Liquid Crystal Polymers (LCPs)
LCPs are a type of polymer that possess superior flexibility and electrical properties. They are also lightweight and provide excellent insulation.
Metal Core
Metal cores are often used in power electronics and high-temperature applications. They provide superior electrical insulation and thermal dissipation.
Glass-clad laminates
Glass-clad laminates are made up of several layers of glass-reinforced plastic and are used in PCBs because they provide low CTE and excellent electrical insulation. Glass-clad laminates are often used in applications that require high temperature stability and high electrical performance.
PCB Dielectric Material Properties
The dielectric properties of a PCB material will affect the electrical properties of the PCB, such as signal integrity, current carrying capacity, and resistance. Each PCB material has different dielectric properties which must be taken into account when designing a PCB. Some important dielectric properties include:
dielectric constant
The most common dielectric property of PCB materials is the dielectric constant, also known as permittivity. This measures how well a material can store an electrical charge and is usually expressed as a number between 1 and 10.
Dielectric strength
Dielectric strength is the maximum voltage that can be applied to the material without causing insulation breakdown.
Dielectric loss
Dielectric loss measures the amount of energy lost in the material due to capacitance and inductance.
Dielectric breakdown voltage
Dielectric breakdown voltage is the voltage at which the material starts to break down.