Checking battery voltage is a crucial skill for car owners and DIY enthusiasts. It helps diagnose battery health and performance issues. A multimeter is the tool you need for this task.
A multimeter measures voltage, current, and resistance. It’s versatile and essential for vehicle maintenance. With it, you can perform a voltmeter battery test easily.
Understanding how to check battery volts with a multimeter can save you time and money. It prevents unexpected breakdowns and extends battery life. Regular testing is key.
This guide will walk you through the process step-by-step. You’ll learn how to prepare your multimeter and interpret the results. Safety tips and troubleshooting advice are also included.
By the end, you’ll be confident in performing a battery voltage test. Let’s get started on ensuring your vehicle’s reliability.
Why Test Battery Voltage?
Testing battery voltage is essential for understanding your battery’s health and performance. A typical fully charged car battery reads about 12.6 volts or higher. If the reading is below 12.4 volts, your battery might be weak or discharged.
Performing a voltmeter battery test with a multimeter can identify potential battery issues. It helps you decide if a battery needs charging, maintenance, or replacement. This test gives you insights into the condition of your vehicle’s electrical systems.
Key benefits of using a multimeter for battery testing include:
- Quick and accurate results
- Prevention of unexpected failures
- Cost-effective maintenance
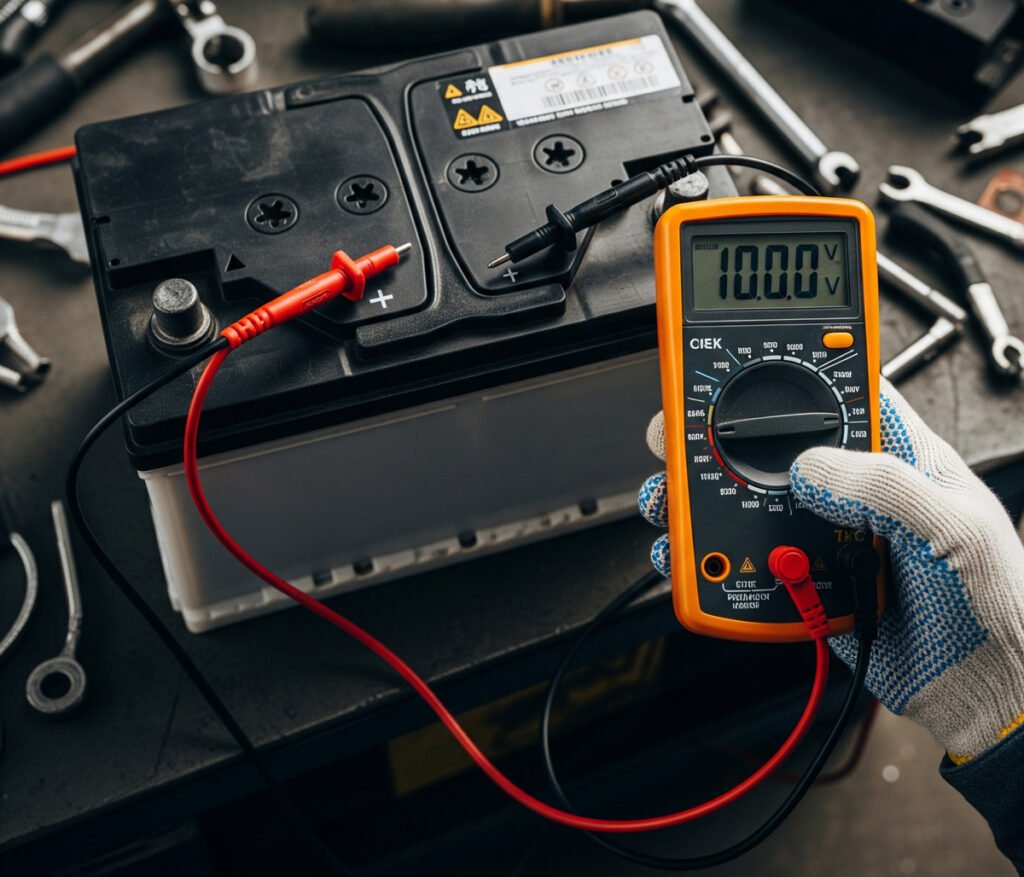

A battery voltage test ensures your car functions reliably. It’s a straightforward but valuable part of vehicle care.
Understanding Battery Voltage: What the Numbers Mean
Battery voltage is a key indicator of battery health. A fully charged car battery typically measures around 12.6 volts. If your reading is significantly lower, it might signal a problem.
Different voltage readings can convey distinct issues. Below are typical interpretations:
- Above 12.6 volts: Battery is fully charged and healthy
- 12.4 to 12.6 volts: Battery is slightly discharged
- Below 12.4 volts: Battery is weak and needs attention

It’s essential to perform voltage tests under consistent conditions. Temperature and other factors can affect readings. Measure your battery in a stable environment for the best results.
Monitoring changes in battery voltage over time helps track performance. Comparing readings allows you to identify patterns or irregularities. This proactive approach can prevent unexpected failures and extend your battery’s lifespan.
Safety Precautions Before Testing
Safety is paramount when working with batteries. Taking precautions can prevent accidents or injuries. Before you start, ensure your workspace is clear and well-lit.
Wear protective gear to guard against potential hazards. Gloves and safety glasses are recommended. They provide a barrier against acid spills or battery sparks.
Here are some key safety precautions:
- Ensure the vehicle and all electronics are off
- Work in a well-ventilated area
- Avoid contact with battery acid
- Ensure the multimeter is in good condition
By following these guidelines, you’ll minimize risks. A careful approach ensures both accurate results and a safe testing process. Remember, staying vigilant about safety is crucial during any battery-related task.
Preparing Your Multimeter for a Battery Voltage Test
To get accurate readings, setting up your multimeter correctly is crucial. Start by checking your multimeter’s battery. A low battery can skew your results.
Set your multimeter to measure DC voltage. This setting is usually marked with a “V” and a straight line. Make sure the multimeter can handle the battery’s voltage range.
Connect the probes to the multimeter’s ports. The red probe should be in the voltage port, while the black goes to the common port. Ensure that the probes are intact and free of damage.

Here’s a quick checklist to prepare your multimeter:
- Check the multimeter’s battery life
- Set it to DC voltage measurement
- Inspect and connect the probes correctly
By preparing your multimeter, you enhance the accuracy of your battery test.
Step-by-Step Guide to Check Battery Volts with a Multimeter
Testing your battery voltage with a multimeter is simple. Begin by ensuring your vehicle is off, and all electrical components are disabled. This prevents any inaccurate readings due to current drain.
Next, locate your car battery. The battery is usually found under the hood, but in some vehicles, it’s in the trunk. Clean the battery terminals to ensure a strong connection.
Turn on your multimeter and double-check it is set to DC volts. The correct setting ensures you measure voltage accurately.
Attach the red probe to the battery’s positive terminal. The positive terminal is typically marked with a plus sign or a red cap. Then connect the black probe to the negative terminal, marked with a minus sign or black cap.
Hold the probes steadily on the terminals as the multimeter displays the voltage reading. This value shows your battery’s current charge level. A healthy car battery will usually read around 12.6 volts or higher.
Keep an eye on the multimeter’s numbers; a drop below 12.4 volts often indicates a weakened battery. Record the reading for future reference. Documenting voltage over time helps you spot trends or problems early.
Here’s a visual rundown of the steps:
- Turn off the car
- Locate and clean battery terminals
- Set multimeter to DC voltage
- Connect red probe to positive, black to negative
- Read and record the voltage
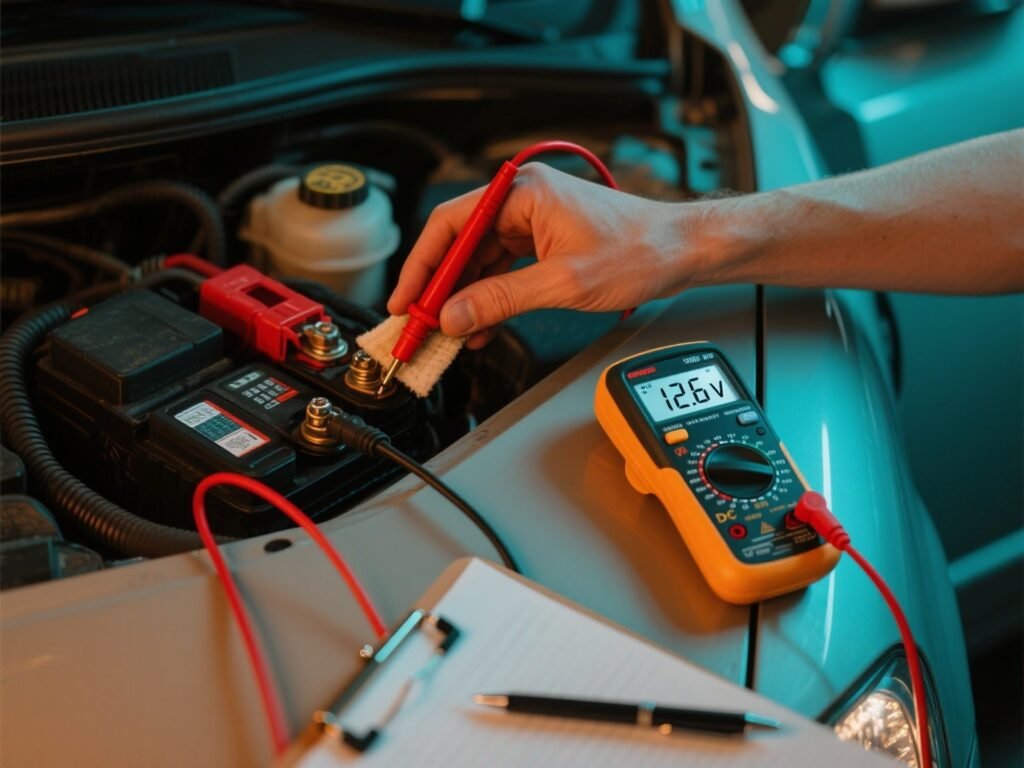

These steps ensure an effective battery voltage test, providing crucial insights into your car’s electrical health. Regular checks help extend your battery’s lifespan and enhance vehicle performance.
Interpreting Your Results: What Your Battery Voltage Tells You
Understanding the numbers on your multimeter is crucial. A fully charged car battery should read around 12.6 volts or higher. This indicates the battery is in good health and fully capable of holding a charge.
If the reading falls between 12.4 and 12.6 volts, it suggests a partially charged battery. This level might still be functional but could benefit from a top-up charge to ensure optimal performance.
A reading below 12.4 volts often signals a weak or discharged battery. This can lead to starting problems or potential breakdowns, indicating it’s time to consider charging or replacement.
Here’s a quick reference:
- 12.6 volts or higher: Fully charged
- 12.4 to 12.6 volts: Partially charged
- Below 12.4 volts: Discharged or weak
By understanding these results, you can take proactive steps to maintain your battery. Consistent monitoring helps in predicting any potential failures, allowing timely actions.
Common Battery Testing Methods Compared
Battery testing methods vary, each with its own benefits. Voltage testing is a quick and non-invasive way to assess battery health. It provides an immediate picture of the charge level and overall battery condition.
Load testing, by contrast, offers a more comprehensive evaluation. This method measures the battery’s ability to deliver power under stress. It can effectively identify deeper issues that aren’t apparent with a simple voltage test.
Hydrometer testing focuses on the battery’s electrolyte fluid, primarily in lead-acid batteries. While detailed, it requires more time and specific equipment.
Here’s a quick comparison:
- Voltage Testing: Quick, easy, non-invasive
- Load Testing: Comprehensive, requires more equipment
- Hydrometer Testing: Detailed, fluid-specific
Choosing the right method depends on your needs and available tools. Each technique offers valuable insights, enhancing overall battery maintenance.
Battery Voltage Troubleshooting
Discovering a low battery voltage isn’t the end of the road. Several steps can help address this issue effectively. Start by checking the battery connections.
Dirty or loose terminals can cause low readings. Clean them thoroughly and ensure secure connections. Next, consider the possibility of a parasitic drain. Some devices may drain the battery when the car is off.
Here’s a quick checklist for troubleshooting:
- Inspect and clean battery terminals
- Check for parasitic drains
- Charge the battery fully
If the voltage remains low after these steps, further diagnostics may be required. Consider professional assistance if these solutions don’t resolve the issue. Proper troubleshooting can extend battery life and reliability.
Choosing the right method depends on your needs and available tools. Each technique offers valuable insights, enhancing overall battery maintenance.
Frequently Asked Questions
Do multimeters work on all types of batteries?
Yes, multimeters can test various battery types, but you might need to adjust the settings depending on the battery.
Can temperature affect voltage readings?
Absolutely. Temperature changes can influence the accuracy of your voltage readings.
Are digital multimeters more accurate?
Generally, digital multimeters are considered more accurate and easier to read than analog multimeters for battery voltage testing.
Can a multimeter test battery life?
While a multimeter can show you the current voltage of a battery, it can’t directly tell you its remaining battery life or capacity. To assess battery life, you’d typically need a specialized battery tester that measures internal resistance or performs a load test.
Is professional testing necessary?
For most common household batteries, DIY testing with a multimeter is sufficient. However, for critical applications, complex battery systems (like those in electric vehicles), or if you suspect a deeper issue, professional testing might be necessary.
Conclusion
Regular battery voltage tests are crucial for maintaining a vehicle’s reliability. By routinely checking your battery, you can catch potential issues before they escalate. This proactive measure can extend the life of your battery and prevent unexpected breakdowns.
Understanding your battery’s health ensures your vehicle operates efficiently. It minimizes the risk of starting problems and other electrical failures. Regular testing is a simple yet effective way to safeguard your vehicle and enhance its performance. Keep your multimeter handy and make battery checks a routine task.